Mefloquine and psychotomimetics share neurotransmitter receptor and transporter interactions in vitro
- PMID: 24488404
- PMCID: PMC4097020
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-014-3446-0
Mefloquine and psychotomimetics share neurotransmitter receptor and transporter interactions in vitro
Abstract
Rationale: Mefloquine is used for the prevention and treatment of chloroquine-resistant malaria, but its use is associated with nightmares, hallucinations, and exacerbation of symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder. We hypothesized that potential mechanisms of action for the adverse psychotropic effects of mefloquine resemble those of other known psychotomimetics.
Objectives: Using in vitro radioligand binding and functional assays, we examined the interaction of (+)- and (-)-mefloquine enantiomers, the non-psychotomimetic anti-malarial agent, chloroquine, and several hallucinogens and psychostimulants with recombinant human neurotransmitter receptors and transporters.
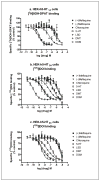
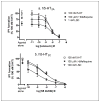
Results: Hallucinogens and mefloquine bound stereoselectively and with relatively high affinity (K i = 0.71-341 nM) to serotonin (5-HT) 2A but not 5-HT1A or 5-HT2C receptors. Mefloquine but not chloroquine was a partial 5-HT2A agonist and a full 5-HT2C agonist, stimulating inositol phosphate accumulation, with similar potency and efficacy as the hallucinogen dimethyltryptamine (DMT). 5-HT receptor antagonists blocked mefloquine's effects. Mefloquine had low or no affinity for dopamine D1, D2, D3, and D4.4 receptors, or dopamine and norepinephrine transporters. However, mefloquine was a very low potency antagonist at the D3 receptor and mefloquine but not chloroquine or hallucinogens blocked [(3)H]5-HT uptake by the 5-HT transporter.
Conclusions: Mefloquine, but not chloroquine, shares an in vitro receptor interaction profile with some hallucinogens and this neurochemistry may be relevant to the adverse neuropsychiatric effects associated with mefloquine use by a small percentage of patients. Additionally, evaluating interactions with this panel of receptors and transporters may be useful for characterizing effects of other psychotropic drugs and for avoiding psychotomimetic effects for new pharmacotherapies, including antimalarial quinolines.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- AlKadi HO. Antimalarial Drug Toxicity: A Review. Chemotherapy. 2007;53:385–391. - PubMed
-
- Amabeoku GJ, Farmer CC. Gamma-aminobutyric acid and mefloquine-induced seizures in mice. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2005;29(6):917–21. - PubMed
-
- Carroll FI, Blackwell JT. Optical isomers of aryl-2-piperidylmethanol antimalarial agents. Preparation, optical purity, and absolute stereochemistry. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 1974;17(2):210–219. - PubMed
-
- Cheng Y, Prusoff WH. Relationship between the inhibition constant (Ki) and the concentration of an inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973;22:3099–3108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

