The Mdm network and its regulation of p53 activities: a rheostat of cancer risk
- PMID: 24488925
- PMCID: PMC4725600
- DOI: 10.1002/humu.22524
The Mdm network and its regulation of p53 activities: a rheostat of cancer risk
Abstract
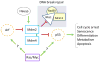
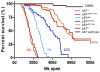
The potent transcriptional activity of p53 (Trp53, TP53) must be kept in check for normal cell growth and survival. Tumors, which drastically deviate from these parameters, have evolved multiple mechanisms to inactivate TP53, the most prevalent of which is the emergence of TP53 missense mutations, some of which have gain-of-function activities. Another important mechanism by which tumors bypass TP53 functions is via increased levels of two TP53 inhibitors, MDM2, and MDM4. Studies in humans and in mice reveal the complexity of TP53 regulation and the exquisite sensitivity of this pathway to small changes in regulation. Here, we summarize the factors that impinge on TP53 activity and thus cell death/arrest or tumor development.
Keywords: Mdm2; Mdm4; TCGA; TP53; Trp53; mouse models; p53.
© 2014 WILEY PERIODICALS, INC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

