GPT2: a glucose 6-phosphate/phosphate translocator with a novel role in the regulation of sugar signalling during seedling development
- PMID: 24489010
- PMCID: PMC3936590
- DOI: 10.1093/aob/mct298
GPT2: a glucose 6-phosphate/phosphate translocator with a novel role in the regulation of sugar signalling during seedling development
Abstract
Background and aims: GPT2, a glucose 6-phosphate/phosphate translocator, plays an important role in environmental sensing in mature leaves of Arabidopsis thaliana. Its expression has also been detected in arabidopsis seeds and seedlings. In order to examine the role of this protein early in development, germination and seedling growth were studied.
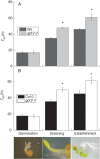
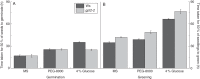
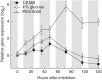
Methods: Germination, greening and establishment of seedlings were monitored in both wild-type Arabidopsis thaliana and in a gpt2 T-DNA insertion knockout line. Seeds were sown on agar plates in the presence or absence of glucose and abscisic acid. Relative expression of GPT2 in seedlings was measured using quantitative PCR.
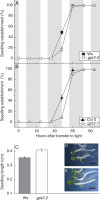
Key results: Plants lacking GPT2 expression were delayed (25-40 %) in seedling establishment, specifically in the process of cotyledon greening (rather than germination). This phenotype could not be rescued by glucose in the growth medium, with greening being hypersensitive to glucose. Germination itself was, however, hyposensitive to glucose in the gpt2 mutant.
Conclusions: The expression of GPT2 modulates seedling development and plays a crucial role in determining the response of seedlings to exogenous sugars during their establishment. This allows us to conclude that endogenous sugar signals function in controlling germination and the transition from heterotrophic to autotrophic growth, and that the partitioning of glucose 6-phosphate, or related metabolites, between the cytosol and the plastid modulates these developmental responses.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana; GPT2; Germination; glucose; greening; seedling development; sugar signalling.
Figures


References
-
- Albrecht V, Ingenfeld A, Apel K. Characterization of the snowy cotyledon 1 mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana: the impact of chloroplast elongation factor G on chloroplast development and plant vitality. Plant Molecular Biology. 2006;60:507–518. - PubMed
-
- Baker A, Graham IA, Holdsworth M, Smith SM, Theodoulou FL. Chewing the fat: β-oxidation in signalling and development. Trends in Plant Science. 2006;11:124–132. - PubMed
-
- Baskin JM, Baskin CC. A classification system for seed dormancy. Seed Science Research. 2004;14:1–16.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

