CD14 mediates binding of high doses of LPS but is dispensable for TNF-α production
- PMID: 24489448
- PMCID: PMC3892557
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/824919
CD14 mediates binding of high doses of LPS but is dispensable for TNF-α production
Abstract
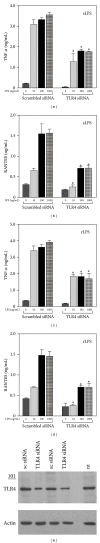
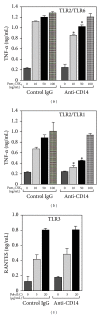
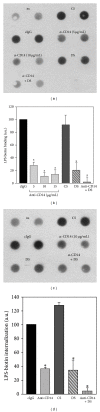
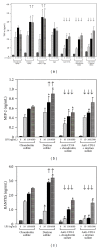
Activation of macrophages with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) involves a sequential engagement of serum LPS-binding protein (LBP), plasma membrane CD14, and TLR4/MD-2 signaling complex. We analyzed participation of CD14 in TNF-α production stimulated with 1-1000 ng/mL of smooth or rough LPS (sLPS or rLPS) and in sLPS binding to RAW264 and J744 cells. CD14 was indispensable for TNF-α generation induced by a low concentration, 1 ng/mL, of sLPS and rLPS. At higher doses of both LPS forms (100-1000 ng/mL), TNF-α release required CD14 to much lower extent. Among the two forms of LPS, rLPS-induced TNF-α production was less CD14-dependent and could proceed in the absence of serum as an LBP source. On the other hand, the involvement of CD14 was crucial for the binding of 1000 ng/mL of sLPS judging from an inhibitory effect of the anti-CD14 antibody. The binding of sLPS was also strongly inhibited by dextran sulfate, a competitive ligand of scavenger receptors (SR). In the presence of dextran sulfate, sLPS-induced production of TNF-α was upregulated about 1.6-fold. The data indicate that CD14 together with SR participates in the binding of high doses of sLPS. However, CD14 contribution to TNF α production induced by high concentrations of sLPS and rLPS can be limited.
Figures


References
-
- Kumar H, Kawai T, Akira S. Pathogen recognition by the innate immune system. International Reviews of Immunology. 2011;30(1):16–34. - PubMed
-
- Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, et al. Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science. 1998;282(5396):2085–2088. - PubMed
-
- Björkbacka H, Fitzgerald KA, Huet F, et al. The induction of macrophage gene expression by LPS predominantly utilizes Myd88-independent signaling cascades. Physiological Genomics. 2004;19(3):319–330. - PubMed
-
- Opal SM, Scannon PJ, Vincent J-L, et al. Relationship between plasma levels of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS-binding protein in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 1999;180(5):1584–1589. - PubMed
-
- Salomao R, Brunialti MK, Rapozo MM, Baggio-Zappia GL, Galanos C, Freudenberg M. Bacterial sensing, cell signaling, and modulation of the immune response during sepsis. Shock. 2012;38(3):227–242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

