Andrographolide, a Novel NF- κ B Inhibitor, Induces Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Apoptosis via a Ceramide-p47phox-ROS Signaling Cascade
- PMID: 24489592
- PMCID: PMC3893871
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/821813
Andrographolide, a Novel NF- κ B Inhibitor, Induces Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Apoptosis via a Ceramide-p47phox-ROS Signaling Cascade
Abstract
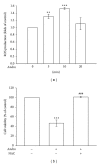
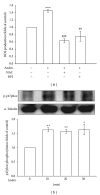
Atherosclerosis is linked with the development of many cardiovascular complications. Abnormal proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) plays a crucial role in the development of atherosclerosis. Accordingly, the apoptosis of VSMCs, which occurs in the progression of vascular proliferation, may provide a beneficial strategy for managing cardiovascular diseases. Andrographolide, a novel nuclear factor- κ B inhibitor, is the most active and critical constituent isolated from the leaves of Andrographis paniculata. Recent studies have indicated that andrographolide is a potential therapeutic agent for treating cancer through the induction of apoptosis. In this study, the apoptosis-inducing activity and mechanisms in andrographolide-treated rat VSMCs were characterized. Andrographolide significantly induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation, p53 activation, Bax, and active caspase-3 expression, and these phenomena were suppressed by pretreating the cells with N-acetyl-L-cysteine, a ROS scavenger, or diphenylene iodonium, a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase (Nox) inhibitor. Furthermore, p47phox, a Nox subunit protein, was phosphorylated in andrographolide-treated rat VSMCs. However, pretreatment with 3-O-methyl-sphingomyelin, a neutral sphingomyelinase inhibitor, significantly inhibited andrographolide-induced p47phox phosphorylation as well as Bax and active caspase-3 expression. Our results collectively demonstrate that andrographolide-reduced cell viability can be attributed to apoptosis in VSMCs, and this apoptosis-inducing activity was associated with the ceramide-p47phox-ROS signaling cascade.
Figures



References
-
- Dzau VJ, Braun-Dullaeus RC, Sedding DG. Vascular proliferation and atherosclerosis: new perspectives and therapeutic strategies. Nature Medicine. 2002;8(11):1249–1256. - PubMed
-
- Mnjoyan ZH, Fujise K. Profound negative regulatory effects by resveratrol on vascular smooth muscle cells: a role of p53-p21WAF1/CIP1 pathway. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2003;311(2):546–552. - PubMed
-
- Walsh K, Smith RC, Kim H-S. Vascular cell apoptosis in remodeling, restenosis, and plaque rupture. Circulation Research. 2000;87(3):184–188. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

