Assessment of the reporting quality of randomized controlled trials on treatment of coronary heart disease with traditional chinese medicine from the chinese journal of integrated traditional and Western medicine: a systematic review
- PMID: 24489719
- PMCID: PMC3904907
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086360
Assessment of the reporting quality of randomized controlled trials on treatment of coronary heart disease with traditional chinese medicine from the chinese journal of integrated traditional and Western medicine: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Due to language limitations, little is known about the reporting quality of randomized clinical trials (RCTs) on the treatment of coronary heart disease (CHD) with traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine (CJITWM).
Objective: In this study, we utilized the CONSORT 2010 statement to understand the reporting quality of RCTs on CHD with TCM from the CJITWM.
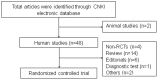
Methods: The China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) electronic database was searched for CJITWM RCTs on the treatment of CHD with TCM, published between January 1, 2006 and December 31, 2011. We excluded articles reported as "animal studies," "topic review," "diagnostic test," "editorials," or "others." The CONSORT checklist was applied to evaluate the reporting quality of all eligible articles by two independent authors after extensive discussion. Each item was graded as either "yes" or "no" depending on whether the authors had reported it or not.
Results: We identified 21 articles meeting our inclusion criteria. The percentage of 11 of the 37 items was 4.8 ∼ 95.2%, 14 of the 37 items were reported in all included articles, while 12 items were not mentioned at all. The average reporting percentage for the "title and abstract" section was 52.4%, for the "introduction" section 100.0%, for the "methods" section 45.4%, for the "results" section 57.1%, for the "discussion" section 79.4%, and for the "other information" section 17.5%.
Conclusion: In general, the reviewed RCTs were not consistent with the CONSORT 2010 statement. Authors should adhere to the CONSORT statement in reporting RCTs; editorial departments may consider the CONSORT statement as a guideline and should instruct authors to write manuscripts, and reviewers to judge them according to CONSORT statutes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of the Reporting Quality of Placebo-controlled Randomized Trials on the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes With Traditional Chinese Medicine in Mainland China: A PRISMA-Compliant Systematic Review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Jan;95(3):e2522. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002522. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 26817893 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the reporting quality of randomized controlled trials on the treatment of diabetes mellitus with traditional chinese medicine: a systematic review.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 24;8(7):e70586. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070586. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23894675 Free PMC article.
-
Consolidated standards of reporting trials (CONSORT) and the completeness of reporting of randomised controlled trials (RCTs) published in medical journals.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Nov 14;11(11):MR000030. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000030.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 23152285 Free PMC article.
-
Do peer reviewers comment on reporting items as instructed by the journal? A secondary analysis of two randomized trials.J Clin Epidemiol. 2025 Jul;183:111818. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2025.111818. Epub 2025 May 8. J Clin Epidemiol. 2025. PMID: 40348145
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
G. sinense and P. notoginseng Extracts Improve Healthspan of Aging Flies and Provide Protection in A Huntington Disease Model.Aging Dis. 2021 Apr 1;12(2):425-440. doi: 10.14336/AD.2020.0714-1. eCollection 2021 Apr. Aging Dis. 2021. PMID: 33815875 Free PMC article.
-
Statin rosuvastatin inhibits apoptosis of human coronary artery endothelial cells through upregulation of the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Sep;22(3):2052-2062. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11266. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32582964 Free PMC article.
-
Technological Advances in Anti-hair Loss and Hair Regrowth Cosmeceuticals: Mechanistic Breakthroughs and Industrial Prospects Driven by Multidisciplinary Collaborative Innovation.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025 Aug 11. doi: 10.1007/s00266-025-05077-3. Online ahead of print. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025. PMID: 40790388 Review.
-
Compliance of Published Randomized Controlled Trials on the Effect of Physical Activity on Primary Dysmenorrhea with the Consortium's Integrated Report on Clinical Trials Statement: A Critical Appraisal of the Literature.Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res. 2020 Nov 7;25(6):445-454. doi: 10.4103/ijnmr.IJNMR_223_19. eCollection 2020 Nov-Dec. Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res. 2020. PMID: 33747832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of the Reporting Quality of Placebo-controlled Randomized Trials on the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes With Traditional Chinese Medicine in Mainland China: A PRISMA-Compliant Systematic Review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Jan;95(3):e2522. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002522. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 26817893 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chan AW, Altman DG (2005) Epidemiology and reporting of randomised trials published in PubMed journals. Lancet 365: 1159–1162. - PubMed
-
- Begg C, Cho M, Eastwood S, Horton R, Moher D, et al. (1996) Improving the quality of reporting of randomized controlled trials. The CONSORT statement. JAMA 276: 637–639. - PubMed
-
- Zhou DZ (2000) Open the gate to the world for traditional Chinese medicine. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine 22: 578–580.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources