Snail contributes to the maintenance of stem cell-like phenotype cells in human pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 24489910
- PMCID: PMC3906155
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087409
Snail contributes to the maintenance of stem cell-like phenotype cells in human pancreatic cancer
Abstract
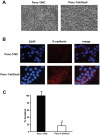
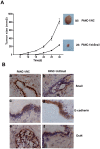
Snail, a potent repressor of E-cadherin expression, plays a key role in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in epithelial cancer. Recently, EMT and stemness programs are found linked together. In the current study, the expression of Snail and its contribution to cancer stem cell (CSC) marker expression, invasiveness, self-renewal, clonogenicity, and tumorigenicity of pancreatic cancer cells were studied. Our results showed that Snail was highly expressed in CSC(high) cell line Panc-1. Stable, short hairpin RNA (shRNA)-mediated Snail knockdown decreased invasion in Panc-1 cells, in line with increased E-cadherin expression and its translocation from the nucleus to the membrane. Snail silencing in Panc-1 also inhibited CSC marker ALDH expression, together with decreased sphere and colony forming capacity, which was highly consistent with the expression of stem cell associated transcription factors like Sox2 and Oct4. In mouse xenograft models, knockdown of Snail led to a reduced number of tumor-bearing mice and a reduced average size of tumors, which had a stronger membrane staining of E-cadherin and lighter staining of Oct4. Collectively, these findings implicate Snail is required for the maintenance of stem cell-like phenotype in pancreatic cancer, and inhibition of Snail could be an efficient strategy to treat pancreatic cancer by targeting CSCs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Coexpression of gene Oct4 and Nanog initiates stem cell characteristics in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition through activation of Stat3/Snail signaling.J Hematol Oncol. 2015 Mar 11;8:23. doi: 10.1186/s13045-015-0119-3. J Hematol Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25879771 Free PMC article.
-
HIF-1α induces the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer stem cells through the Snail pathway.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 7;8(6):9535-9545. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14484. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28076840 Free PMC article.
-
Polyphenols from marine brown algae target radiotherapy-coordinated EMT and stemness-maintenance in residual pancreatic cancer.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015 Sep 22;6(1):182. doi: 10.1186/s13287-015-0173-3. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 26395574 Free PMC article.
-
Embryonic stem cell factors and pancreatic cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Mar 7;20(9):2247-54. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i9.2247. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24605024 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer.Adv Cancer Res. 2023;159:37-73. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2023.02.008. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Adv Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37268401 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-148a-3p suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stemness properties via Wnt1-mediated Wnt/β-catenin pathway in pancreatic cancer.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Nov;24(22):13020-13035. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15900. Epub 2020 Oct 7. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 33026174 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA MALAT-1 enhances stem cell-like phenotypes in pancreatic cancer cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Mar 24;16(4):6677-93. doi: 10.3390/ijms16046677. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25811929 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic Plasticity: Driver of Cancer Initiation, Progression, and Therapy Resistance.Cell Stem Cell. 2019 Jan 3;24(1):65-78. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2018.11.011. Epub 2018 Dec 13. Cell Stem Cell. 2019. PMID: 30554963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Cancer Stem Cells as the Key Driver of Carcinogenesis and Therapeutic Resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 16;24(2):1786. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021786. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36675306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of modulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulators Snail1 and Snail2 on cancer cell radiosensitivity by targeting of the cell cycle, cell apoptosis and cell migration/invasion.Oncol Lett. 2019 Jan;17(1):23-30. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9636. Epub 2018 Oct 29. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 30655734 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A (2012) Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 62: 10–29. - PubMed
-
- Magee CJ, Ghaneh P, Neoptolemos JP (2002) Surgical and medical therapy for pancreatic carcinoma. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 16: 435–455. - PubMed
-
- Jones RJ, Matsui WH, Smith BD (2004) Cancer stem cells: are we missing the target? J Natl Cancer Inst 96: 583–585. - PubMed
-
- Kurrey NK, Jalgaonkar SP, Joglekar AV, Ghanate AD, Chaskar PD, et al. (2009) Snail and slug mediate radioresistance and chemoresistance by antagonizing p53-mediated apoptosis and acquiring a stem-like phenotype in ovarian cancer cells. Stem Cells 27: 2059–2068. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

