IKK2 inhibition attenuates laser-induced choroidal neovascularization
- PMID: 24489934
- PMCID: PMC3905033
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087530
IKK2 inhibition attenuates laser-induced choroidal neovascularization
Abstract
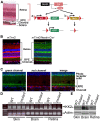
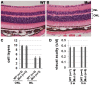
Choroidal neovascularization (CNV) is aberrant angiogenesis associated with exudative age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a leading cause of blindness in the elderly. Inflammation has been suggested as a risk factor for AMD. The IKK2/NF-κB pathway plays a key role in the inflammatory response through regulation of the transcription of cytokines, chemokines, growth factors and angiogenic factors. We investigated the functional role of IKK2 in development of the laser-induced CNV using either Ikk2 conditional knockout mice or an IKK2 inhibitor. The retinal neuronal tissue and RPE deletion of IKK2 was generated by breeding Ikk2(-/flox) mice with Nestin-Cre mice. Deletion of Ikk2 in the retina caused no obvious defect in retinal development or function, but resulted in a significant reduction in laser-induced CNV. In addition, intravitreal or retrobulbar injection of an IKK2 specific chemical inhibitor, TPCA-1, also showed similar inhibition of CNV. Furthermore, in vitro inhibition of IKK2 in ARPE-19 cells significantly reduced heat shock-induced expression of NFKBIA, IL1B, CCL2, VEGFA, PDGFA, HIF1A, and MMP-2, suggesting that IKK2 may regulate multiple molecular pathways involved in laser-induced CNV. The in vivo laser-induced expression of VEGFA, and HIF1A in RPE and choroidal tissue was also blocked by TPCA-1 treatment. Thus, IKK2/NF-κB signaling appears responsible for production of pro-inflammatory and pro-angiogenic factors in laser-induced CNV, suggesting that this intracellular pathway may serve as an important therapeutic target for aberrant angiogenesis in exudative AMD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
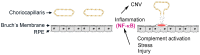




References
-
- Rattner A, Nathans J (2006) Macular degeneration: recent advances and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Neurosci 7: 860–872. - PubMed
-
- Brown DM, Kaiser PK, Michels M, Soubrane G, Heier JS, et al. (2006) Ranibizumab versus verteporfin for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. N Engl J Med 355: 1432–1444. - PubMed
-
- Gragoudas ES, Adamis AP, Cunningham ET Jr, Feinsod M, Guyer DR (2004) Pegaptanib for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. N Engl J Med 351: 2805–2816. - PubMed
-
- Rosenfeld PJ, Brown DM, Heier JS, Boyer DS, Kaiser PK, et al. (2006) Ranibizumab for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. N Engl J Med 355: 1419–1431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

