Serum CXCL16 as a novel marker of renal injury in type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 24489966
- PMCID: PMC3906379
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087786
Serum CXCL16 as a novel marker of renal injury in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Background: Soluble C-X-C chemokine ligand 16 (CXCL16), a scavenger receptor for oxidized low density lipoprotein, has been shown to promote atherogenic effects in vivo and to predict long-term mortality in acute coronary syndrome. The aim of this study was to explore the association of circulating CXCL16 levels with diabetic subjects with and without renal disease.
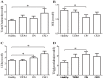
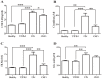
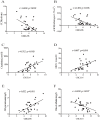
Methodology/principal findings: One hundred twenty Chinese subjects, which included patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), diabetic nephropathy (DN), and CKD, as well as healthy controls, were enrolled in this study. Serum CXCL16 levels were examined by immunoassay and other clinical biochemical parameters were tested based on standard methods. Our results indicated that, HDL and LDL cholesterol levels are significantly different in DN but not in T2D patients in comparison with healthy subjects. On the other hand, Serum CXCL16 levels were significantly increased in DN subjects compared with age and gender matched healthy and T2DM subjects (p<0.05 respectively). However, no significant changes in serum CXCL16 levels were found between T2DM and healthy subjects. Furthermore, serum CXCL16 concentration negatively correlated with estimated glomerular filtrate rate, creatinine clearance rate and blood albumin, and positively with 24 h proteinuria, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine, and uric acid after adjusting for age, gender and BMI in subjects with DN. Multiple stepwise regression analyses indicated that serum CXCL16 levels were independently associated with serum 24 h proteinuria, and BUN (p<0.05 respectively).
Conclusion: Serum CXCL16 may be an indicator of renal injury in subjects with T2DM. Understanding the exact mechanism of elevated CXCL16 in subjects with DN requires further study.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum CXCL16 as a Novel Biomarker of Coronary Artery Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: a Pilot Study.Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2016 Spring;46(2):184-9. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2016. PMID: 27098626
-
Soluble C-X-C chemokine ligand 16 levels are increased in gout patients.Clin Biochem. 2012 Nov;45(16-17):1368-73. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2012.05.014. Epub 2012 May 22. Clin Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22627199
-
Osteoinductive factor is a novel biomarker for the diagnosis of early diabetic nephropathy.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Mar 1;8(3):3110-5. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26045825 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating CXCL16 in Diabetic Kidney Disease.Kidney Blood Press Res. 2016;41(5):663-671. doi: 10.1159/000447935. Epub 2016 Sep 26. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2016. PMID: 27665581
-
Can Lipoprotein(a) Predict the Risk of Diabetic Nephropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus?: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Horm Metab Res. 2025 Apr;57(4):242-251. doi: 10.1055/a-2554-0696. Epub 2025 Apr 10. Horm Metab Res. 2025. PMID: 40209745
Cited by
-
The DRF motif of CXCR6 as chemokine receptor adaptation to adhesion.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 7;12(3):e0173486. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173486. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28267793 Free PMC article.
-
Cxcr6-Based Mesenchymal Stem Cell Gene Therapy Potentiates Skin Regeneration in Murine Diabetic Wounds.Mol Ther. 2020 May 6;28(5):1314-1326. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.02.014. Epub 2020 Feb 14. Mol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32112713 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of pattern recognition receptors in diabetic nephropathy.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2020 Mar.;21(3):192-203. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1900490. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2020. PMID: 32133797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resveratrol Inhibited ADAM10 Mediated CXCL16-Cleavage and T-Cells Recruitment to Pancreatic β-Cells in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus in Mice.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Mar 9;14(3):594. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14030594. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35335970 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the CXCL16/CXCR6 pathway promotes lipid deposition in fatty livers of apolipoprotein E knockout mice and HepG2 cells.Am J Transl Res. 2018 Jun 15;10(6):1802-1816. eCollection 2018. Am J Transl Res. 2018. PMID: 30018721 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agostini C, Cabrelle A, Calabrese F, Bortoli M, Scquizzato E, et al. (2005) Role for CXCR6 and its ligand CXCL16 in the pathogenesis of T-cell alveolitis in sarcoidosis. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine 172: 1290–1298. - PubMed
-
- Aslanian AM, Charo IF (2006) Targeted disruption of the scavenger receptor and chemokine CXCL16 accelerates atherosclerosis. Circulation 114: 583–590. - PubMed
-
- Moore KJ, Freeman MW (2006) Scavenger receptors in atherosclerosis: beyond lipid uptake. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology 26: 1702–1711. - PubMed
-
- Sheikine Y, Sirsjo A (2008) CXCL16/SR-PSOX–a friend or a foe in atherosclerosis? Atherosclerosis 197: 487–495. - PubMed
-
- Wuttge DM, Zhou X, Sheikine Y, Wagsater D, Stemme V, et al. (2004) CXCL16/SR-PSOX is an interferon-gamma-regulated chemokine and scavenger receptor expressed in atherosclerotic lesions. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology 24: 750–755. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

