Overcoming intrinsic inhibitory pathways to augment the antineoplastic activity of adoptively transferred T cells: Re-tuning your CAR before hitting a rocky road
- PMID: 24490126
- PMCID: PMC3897565
- DOI: 10.4161/onci.26492
Overcoming intrinsic inhibitory pathways to augment the antineoplastic activity of adoptively transferred T cells: Re-tuning your CAR before hitting a rocky road
Abstract
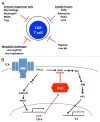
Effector T cells become rapidly inactivated after antigen exposure due to extracellular as well as intrinsic signals. We have recently demonstrated that the deletion of diacylglycerol kinases, intrinsic inhibitors of T-cell signaling, enhances the activity of adoptively transferred T cells expressing a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) specific for a tumor-associated antigen.
Keywords: Chimeric Antigen Receptor; T cell hypofunction; diacylglycerol kinase; tumor immunosuppression; tumor microenvironment.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
