Immunosuppression abrogates resistance of young rabbits to Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease (RHD)
- PMID: 24490832
- PMCID: PMC3926702
- DOI: 10.1186/1297-9716-45-14
Immunosuppression abrogates resistance of young rabbits to Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease (RHD)
Abstract
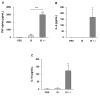
Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease (RHD) is caused by a calicivirus (RHDV) that kills 90% of infected adult European rabbits within 3 days. Remarkably, young rabbits are resistant to RHD. We induced immunosuppression in young rabbits by treatment with methylprednisolone acetate (MPA) and challenged the animals with RHDV by intramuscular injection. All of these young rabbits died within 3 days of infection due to fulminant hepatitis, presenting a large number of RHDV-positive dead or apoptotic hepatocytes, and a significant seric increase in cytokines, features that are similar to those of naïve adult rabbits infected by RHDV. We conclude that MPA-induced immunosuppression abrogates the resistance of young rabbits to RHD, indicating that there are differences in the innate immune system between young and adult rabbits that contribute to their distinct resistance/susceptibility to RHDV infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rabbit haemorrhagic disease (RHD) and rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV): a review.Vet Res. 2012 Feb 10;43(1):12. doi: 10.1186/1297-9716-43-12. Vet Res. 2012. PMID: 22325049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adult rabbits acquire resistance to lethal calicivirus infection by adoptive transfer of sera from infected young rabbits.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2008 Feb 15;121(3-4):364-9. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2007.09.005. Epub 2007 Oct 2. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2008. PMID: 17980918
-
Early inflammatory response of young rabbits attending natural resistance to calicivirus (RHDV) infection.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2012 Dec 15;150(3-4):181-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2012.09.038. Epub 2012 Oct 2. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2012. PMID: 23092749
-
Rabbit haemorrhagic disease: advantages of cELISA in assessing immunity in wild rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus).Vet Microbiol. 2011 Dec 15;153(3-4):387-92. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2011.05.049. Epub 2011 Jun 12. Vet Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21719216
-
The importance of liver lesions and changes to biochemical and coagulation factors in the pathogenesis of RHD.Acta Biochim Pol. 2015;62(2):169-71. doi: 10.18388/abp.2014_943. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Acta Biochim Pol. 2015. PMID: 25918886 Review.
Cited by
-
A Review on the Methods Used for the Detection and Diagnosis of Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus (RHDV).Microorganisms. 2021 Apr 30;9(5):972. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9050972. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33946292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Practical Suggestions for Assessing Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease Virus 2 Risk to Endangered Native Lagomorphs in North America and Southern Africa.Viruses. 2024 Aug 15;16(8):1299. doi: 10.3390/v16081299. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39205273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Full-genome sequencing of German rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus uncovers recombination between RHDV (GI.2) and EBHSV (GII.1).Virus Evol. 2020 Nov 24;6(2):veaa080. doi: 10.1093/ve/veaa080. eCollection 2020 Jul. Virus Evol. 2020. PMID: 33324492 Free PMC article.
-
Robust Innate Immunity of Young Rabbits Mediates Resistance to Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Caused by Lagovirus Europaeus GI.1 But Not GI.2.Viruses. 2018 Sep 19;10(9):512. doi: 10.3390/v10090512. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30235853 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and Initial Testing of a Medium-Sized, Surgically Feasible Animal Model for Brucellar Spondylodiscitis: A Preliminary Study.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Sep 30;2019:7368627. doi: 10.1155/2019/7368627. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31662995 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferreira PG, Costa-e-Silva A, Monteiro E, Oliveira MJ, Aguas AP. Transient decrease in blood heterophils and sustained liver damage caused by calicivirus infection of young rabbits that are naturally resistant to rabbit haemorrhagic disease. Res Vet Sci. 2004;76:83–94. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2003.08.003. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

