Engineered nanoparticles interacting with cells: size matters
- PMID: 24491160
- PMCID: PMC3922601
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-3155-12-5
Engineered nanoparticles interacting with cells: size matters
Abstract
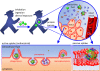
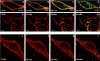
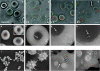
With the rapid advancement of nanoscience and nanotechnology, detailed knowledge of interactions between engineered nanomaterials and cells, tissues and organisms has become increasingly important, especially in regard to possible hazards to human health. This review intends to give an overview of current research on nano-bio interactions, with a focus on the effects of NP size on their interactions with live cells. We summarize common techniques to characterize NP size, highlight recent work on the impact of NP size on active and passive cellular internalization and intracellular localization. Cytotoxic effects are also discussed.
Figures

References
-
- Astruc D. In: Nanoparticles and Catalysis. Astruc D, editor. KGaA, Weinheim: WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co; 2008. Transition - metal nanoparticles in catalysis: from historical background to the state - of - the art.
-
- Stratakis E, Kymakis E. Nanoparticle-based plasmonic organic photovoltaic devices. Mater Today. 2013;16:133–146. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2013.04.006. - DOI
-
- Meng FH, Cheng R, Deng C, Zhong ZY. Intracellular drug release nanosystems. Mater Today. 2012;15:436–442. doi: 10.1016/S1369-7021(12)70195-5. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

