Discovery of a potent stapled helix peptide that binds to the 70N domain of replication protein A
- PMID: 24491171
- PMCID: PMC3969094
- DOI: 10.1021/jm401730y
Discovery of a potent stapled helix peptide that binds to the 70N domain of replication protein A
Abstract
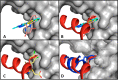
Stapled helix peptides can serve as useful tools for inhibiting protein-protein interactions but can be difficult to optimize for affinity. Here we describe the discovery and optimization of a stapled helix peptide that binds to the N-terminal domain of the 70 kDa subunit of replication protein A (RPA70N). In addition to applying traditional optimization strategies, we employed a novel approach for efficiently designing peptides containing unnatural amino acids. We discovered hot spots in the target protein using a fragment-based screen, identified the amino acid that binds to the hot spot, and selected an unnatural amino acid to incorporate, based on the structure-activity relationships of small molecules that bind to this site. The resulting stapled helix peptide potently and selectively binds to RPA70N, does not disrupt ssDNA binding, and penetrates cells. This peptide may serve as a probe to explore the therapeutic potential of RPA70N inhibition in cancer.
Figures



References
-
- Wold M. S. Replication protein A: a heterotrimeric, single-stranded DNA-binding protein required for eukaryotic DNA metabolism. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1997, 66, 61–92. - PubMed
-
- Majka J.; Binz S. K.; Wold M. S.; Burgers P. M. Replication protein A directs loading of the DNA damage checkpoint clamp to 5′-DNA junctions. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 27855–27861. - PubMed
-
- Cortez D.; Guntuku S.; Qin J.; Elledge S. J. ATR and ATRIP: partners in checkpoint signaling. Science 2001, 294, 1713–1716. - PubMed
-
- Bartkova J.; Horejsi Z.; Koed K.; Kramer A.; Tort F.; Zieger K.; Guldberg P.; Sehested M.; Nesland J. M.; Lukas C.; Orntoft T.; Lukas J.; Bartek J. DNA damage response as a candidate anti-cancer barrier in early human tumorigenesis. Nature 2005, 434, 864–870. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- DP1 CA174419/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM065484/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA102792/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA102729/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA174887/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA092584/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 11566/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- CA102792/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES000267/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008320/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 ES021690/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 ES007028/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

