Quantum mechanical studies of DNA and LNA
- PMID: 24491259
- PMCID: PMC3962643
- DOI: 10.1089/nat.2013.0465
Quantum mechanical studies of DNA and LNA
Abstract
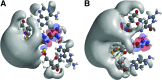
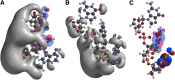
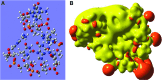
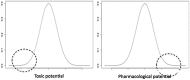
Quantum mechanical (QM) methodology has been employed to study the structure activity relations of DNA and locked nucleic acid (LNA). The QM calculations provide the basis for construction of molecular structure and electrostatic surface potentials from molecular orbitals. The topologies of the electrostatic potentials were compared among model oligonucleotides, and it was observed that small structural modifications induce global changes in the molecular structure and surface potentials. Since ligand structure and electrostatic potential complementarity with a receptor is a determinant for the bonding pattern between molecules, minor chemical modifications may have profound changes in the interaction profiles of oligonucleotides, possibly leading to changes in pharmacological properties. The QM modeling data can be used to understand earlier observations of antisense oligonucleotide properties, that is, the observation that small structural changes in oligonucleotide composition may lead to dramatic shifts in phenotypes. These observations should be taken into account in future oligonucleotide drug discovery, and by focusing more on non RNA target interactions it should be possible to utilize the exhibited property diversity of oligonucleotides to produce improved antisense drugs.
Figures



References
-
- ABDALI S., JALKANEN K.J., BOHR H., SUHAI S., and NIEMINEN R.M. (2002). The VA and VCD spectra of various isotopes of L-alanine in aqueous solution. Chem. Phys. 282,219–235
-
- ALTMANN K.-H., DEAN N.M., FABBRO D., FREIER S.M., GEIGER T., HÄNER R., HÜSKEN D., MARTIN P., MONIA B.P., MÜLLER M., et al. (1996). Second generation OD antisense oligonucleotides: from nuclease resistance to biological efficacy in animals. Chimia 50,168–176
-
- BOHR H.G. (2013). Perspectives in quantum nanobiology and biophysical chemistry. Current Phys. Chem. 3,4–8
-
- BURGOYNE N.J., and JACKSON R.M. (2006). Predicting protein interaction sites: binding hot-spots in protein-protein and protein-ligand interfaces. Bioinformatics 22,1335–1342 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
