Multisensory maps in parietal cortex
- PMID: 24492077
- PMCID: PMC3969294
- DOI: 10.1016/j.conb.2013.08.014
Multisensory maps in parietal cortex
Abstract
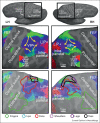
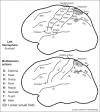
Parietal cortex has long been known to be a site of sensorimotor integration. Recent findings in humans have shown that it is divided up into a number of small areas somewhat specialized for eye movements, reaching, and hand movements, but also face-related movements (avoidance, eating), lower body movements, and movements coordinating multiple body parts. The majority of these areas contain rough sensory (receptotopic) maps, including a substantial multisensory representation of the lower body and lower visual field immediately medial to face VIP. There is strong evidence for retinotopic remapping in LIP and face-centered remapping in VIP, and weaker evidence for hand-centered remapping. The larger size of the functionally distinct inferior parietal default mode network in humans compared to monkeys results in a superior and medial displacement of middle parietal areas (e.g., the saccade-related LIP's). Multisensory superior parietal areas located anterior to the angular gyrus such as AIP and VIP are less medially displaced relative to macaque monkeys, so that human LIP paradoxically ends up medial to human VIP.
Copyright © 2013 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cortical connections of parietal field PEc in the macaque: linking vision and somatic sensation for the control of limb action.Cereb Cortex. 2010 Nov;20(11):2592-604. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhq007. Epub 2010 Feb 22. Cereb Cortex. 2010. PMID: 20176687
-
A comparison of frontoparietal fMRI activation during anti-saccades and anti-pointing.J Neurophysiol. 2000 Sep;84(3):1645-55. doi: 10.1152/jn.2000.84.3.1645. J Neurophysiol. 2000. PMID: 10980034 Clinical Trial.
-
The functional organization of the intraparietal sulcus in humans and monkeys.J Anat. 2005 Jul;207(1):3-17. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2005.00426.x. J Anat. 2005. PMID: 16011542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mapping the complex topological organization of the human parietal face area.Neuroimage. 2017 Dec;163:459-470. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.09.004. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Neuroimage. 2017. PMID: 28889002 Free PMC article.
-
Parietal encoding of action in depth.Neuropsychologia. 2009 May;47(6):1409-20. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2008.12.028. Epub 2008 Dec 30. Neuropsychologia. 2009. PMID: 19154747 Review.
Cited by
-
Generalization in category learning: the roles of representational and decisional uncertainty.J Neurosci. 2015 Jun 10;35(23):8802-12. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0654-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26063914 Free PMC article.
-
Task-specificity in focal dystonia is shaped by aberrant diversity of a functional network kernel.Mov Disord. 2018 Dec;33(12):1918-1927. doi: 10.1002/mds.97. Epub 2018 Sep 27. Mov Disord. 2018. PMID: 30264427 Free PMC article.
-
Shared neural underpinnings of multisensory integration and trial-by-trial perceptual recalibration in humans.Elife. 2019 Jun 27;8:e47001. doi: 10.7554/eLife.47001. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31246172 Free PMC article.
-
Auditory Spatial Coding Flexibly Recruits Anterior, but Not Posterior, Visuotopic Parietal Cortex.Cereb Cortex. 2016 Mar;26(3):1302-1308. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhv303. Epub 2015 Dec 11. Cereb Cortex. 2016. PMID: 26656996 Free PMC article.
-
Reward-based option competition in human dorsal stream and transition from stochastic exploration to exploitation in continuous space.Sci Adv. 2024 Feb 23;10(8):eadj2219. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adj2219. Epub 2024 Feb 23. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38394198 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang Q., Sporns O., Burkhalter A: Network analysis of corticocortical connections reveals ventral and dorsal processing streams in mouse visual cortex. J Neurosci. 2012;32:4386–4399. - PMC - PubMed
-
Contains a comprehensive catalog of visual area connections from flatmounted cortex including multisensory areas RL and A in mice and shows that visual areas are closer to being fully interconnected in mice than in monkeys.
-
- Markov N.T., Ercsey-Ravasz M.M., Ribeiro Gomes A.R., Lamy C., Magrou L., Vezoli J., Misery P., Falchier A., Quilodran R., Gariel M.A. A weighted and directed interareal connectivity matrix for macaque cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex. 2012 [September 25, Epub ahead of print] - PMC - PubMed
-
Contains a comprehensive catalog of visual area connections in macaque monkeys including of which 30% have not been previously reported. The great majority of connections come from areas within 12 mm of the injection site. Compare with [1].
-
- Ghazanfar A.A., Schroeder CE: Is neocortex essentially multisensory? Trends Cogn Sci. 2006;10:278–285. - PubMed
-
- Shams L., Kim R: Crossmodal influences on visual perception. Phys Life Rev. 2010;7:269–284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

