Blocking CD40-TRAF6 signaling is a therapeutic target in obesity-associated insulin resistance
- PMID: 24492375
- PMCID: PMC3932883
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1400419111
Blocking CD40-TRAF6 signaling is a therapeutic target in obesity-associated insulin resistance
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Mar 25;111(12):4644. Schulte, Klaus [corrected to Schulte, Klaus-Martin]
Abstract
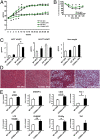
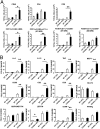
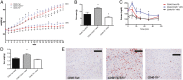
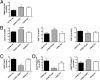
The immune system plays an instrumental role in obesity and insulin resistance. Here, we unravel the role of the costimulatory molecule CD40 and its signaling intermediates, TNF receptor-associated factors (TRAFs), in diet-induced obesity (DIO). Although not exhibiting increased weight gain, male CD40(-/-) mice in DIO displayed worsened insulin resistance, compared with wild-type mice. This worsening was associated with excessive inflammation of adipose tissue (AT), characterized by increased accumulation of CD8(+) T cells and M1 macrophages, and enhanced hepatosteatosis. Mice with deficient CD40-TRAF2/3/5 signaling in MHCII(+) cells exhibited a similar phenotype in DIO as CD40(-/-) mice. In contrast, mice with deficient CD40-TRAF6 signaling in MHCII(+) cells displayed no insulin resistance and showed a reduction in both AT inflammation and hepatosteatosis in DIO. To prove the therapeutic potential of inhibition of CD40-TRAF6 in obesity, DIO mice were treated with a small-molecule inhibitor that we designed to specifically block CD40-TRAF6 interactions; this compound improved insulin sensitivity, reduced AT inflammation, and decreased hepatosteatosis. Our study reveals that the CD40-TRAF2/3/5 signaling pathway in MHCII(+) cells protects against AT inflammation and metabolic complications associated with obesity whereas CD40-TRAF6 interactions in MHCII(+) cells aggravate these complications. Inhibition of CD40-TRAF6 signaling by our compound may provide a therapeutic option in obesity-associated insulin resistance.
Keywords: immunity; metabolism; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Osborn O, Sears DD, Olefsky JM. Fat-induced inflammation unchecked. Cell Metab. 2010;12(6):553–554. - PubMed
-
- Chatzigeorgiou A, Karalis KP, Bornstein SR, Chavakis T. Lymphocytes in obesity-related adipose tissue inflammation. Diabetologia. 2012;55(10):2583–2592. - PubMed
-
- Gregor MF, Hotamisligil GS. Inflammatory mechanisms in obesity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2011;29:415–445. - PubMed
-
- Nishimura S, et al. CD8+ effector T cells contribute to macrophage recruitment and adipose tissue inflammation in obesity. Nat Med. 2009;15(8):914–920. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

