Blunted sympathoinhibitory responses in obesity-related hypertension are due to aberrant central but not peripheral signalling mechanisms
- PMID: 24492842
- PMCID: PMC3979620
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.269670
Blunted sympathoinhibitory responses in obesity-related hypertension are due to aberrant central but not peripheral signalling mechanisms
Abstract
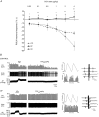
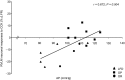
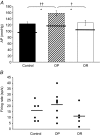
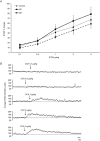
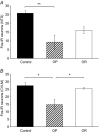
The gut hormone cholecystokinin (CCK) acts at subdiaphragmatic vagal afferents to induce renal and splanchnic sympathoinhibition and vasodilatation, via reflex inhibition of a subclass of cardiovascular-controlling neurons in the rostroventrolateral medulla (RVLM). These sympathoinhibitory and vasodilator responses are blunted in obese, hypertensive rats and our aim in the present study was to determine whether this is attributable to (i) altered sensitivity of presympathetic vasomotor RVLM neurons, and (ii) aberrant peripheral or central signalling mechanisms. Using a diet-induced obesity model, male Sprague-Dawley rats exhibited either an obesity-prone (OP) or obesity-resistant (OR) phenotype when placed on a medium high fat diet for 13-15 weeks; control animals were placed on a low fat diet. OP animals had elevated resting arterial pressure compared to OR/control animals (P < 0.05). Barosensitivity of RVLM neurons was significantly attenuated in OP animals (P < 0.05), suggesting altered baroreflex gain. CCK induced inhibitory responses in RVLM neurons of OR/control animals but not OP animals. Subdiaphragmatic vagal nerve responsiveness to CCK and CCK1 receptor mRNA expression in nodose ganglia did not differ between the groups, but CCK induced significantly less Fos-like immunoreactivity in both the nucleus of the solitary tract and the caudal ventrolateral medulla of OP animals compared to controls (P < 0.05). These results suggest that blunted sympathoinhibitory and vasodilator responses in obesity-related hypertension are due to alterations in RVLM neuronal responses, resulting from aberrant central but not peripheral signalling mechanisms. In obesity, blunted sympathoinhibitory mechanisms may lead to increased regional vascular resistance and contribute to the development of hypertension.
Figures
References
-
- Burman KJ, Sartor DM, Verberne AJ, Llewellyn-Smith IJ. Cocaine-and amphetamine-regulated transcript in catecholamine and noncatecholamine presympathetic vasomotor neurons of rat rostral ventrolateral medulla. J Comp Neurol. 2004;476:19–31. - PubMed
-
- Caprio S, Daniels SR, Drewnowski A, Kaufman FR, Palinkas LA, Rosenbloom AL. Influence of race, ethnicity, and culture on childhood obesity: implications for prevention and treatment: a consensus statement of Shaping America's Health and the Obesity Society. Diab Care. 2008;31:2211–2221. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cates MJ, Dickinson CJ, Hart EC, Paton JF. Neurogenic hypertension and elevated vertebrobasilar arterial resistance: is there a causative link. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2012;14:261–269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

