Candida-elicited murine Th17 cells express high Ctla-4 compared with Th1 cells and are resistant to costimulation blockade
- PMID: 24493820
- PMCID: PMC4071624
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301332
Candida-elicited murine Th17 cells express high Ctla-4 compared with Th1 cells and are resistant to costimulation blockade
Abstract
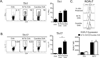
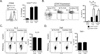
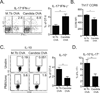
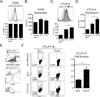
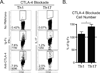
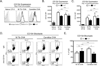
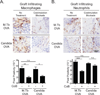
Effector and memory T cells may cross-react with allogeneic Ags to mediate graft rejection. Whereas the costimulation properties of Th1 cells are well studied, relatively little is known about the costimulation requirements of microbe-elicited Th17 cells. The costimulation blocker CTLA-4 Ig has been ineffective in the treatment of several Th17-driven autoimmune diseases and is associated with severe acute rejection following renal transplantation, leading us to investigate whether Th17 cells play a role in CD28/CTLA-4 blockade-resistant alloreactivity. We established an Ag-specific model in which Th1 and Th17 cells were elicited via Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Candida albicans immunization, respectively. C. albicans immunization elicited a higher frequency of Th17 cells and conferred resistance to costimulation blockade following transplantation. Compared with the M. tuberculosis group, C. albicans-elicited Th17 cells contained a higher frequency of IL-17(+)IFN-γ(+) producers and a lower frequency of IL-10(+) and IL-10(+)IL-17(+) cells. Importantly, Th17 cells differentially regulated the CD28/CTLA-4 pathway, expressing similarly high CD28 but significantly greater amounts of CTLA-4 compared with Th1 cells. Ex vivo blockade experiments demonstrated that Th17 cells are more sensitive to CTLA-4 coinhibition and therefore less susceptible to CTLA-4 Ig. These novel insights into the differential regulation of CTLA-4 coinhibition on CD4(+) T cells have implications for the immunomodulation of pathologic T cell responses during transplantation and autoimmunity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
High CTLA-4 expression on Th17 cells results in increased sensitivity to CTLA-4 coinhibition and resistance to belatacept.Am J Transplant. 2014 Mar;14(3):607-14. doi: 10.1111/ajt.12600. Am J Transplant. 2014. PMID: 24730049 Free PMC article.
-
Selective CD28 blockade attenuates CTLA-4-dependent CD8+ memory T cell effector function and prolongs graft survival.JCI Insight. 2018 Jan 11;3(1):e96378. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.96378. eCollection 2018 Jan 11. JCI Insight. 2018. PMID: 29321374 Free PMC article.
-
Differential requirements for Th1 and Th17 responses to a systemic self-antigen.J Immunol. 2011 Apr 15;186(8):4668-73. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003786. Epub 2011 Mar 14. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21402892
-
Complexities of CD28/B7: CTLA-4 costimulatory pathways in autoimmunity and transplantation.Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:225-52. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.19.1.225. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11244036 Review.
-
A role for Th1-like Th17 cells in the pathogenesis of inflammatory and autoimmune disorders.Mol Immunol. 2019 Jan;105:107-115. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2018.11.015. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Mol Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30502718 Review.
Cited by
-
Memory T cell-mediated rejection is mitigated by FcγRIIB expression on CD8+ T cells.Am J Transplant. 2020 Aug;20(8):2206-2215. doi: 10.1111/ajt.15837. Epub 2020 Mar 24. Am J Transplant. 2020. PMID: 32154641 Free PMC article.
-
Cell wall mannan of Candida krusei mediates dendritic cell apoptosis and orchestrates Th17 polarization via TLR-2/MyD88-dependent pathway.Sci Rep. 2018 Nov 20;8(1):17123. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35101-3. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30459422 Free PMC article.
-
IL-6 inhibition prevents costimulation blockade-resistant allograft rejection in T cell-depleted recipients by promoting intragraft immune regulation in mice.Nat Commun. 2024 Jun 3;15(1):4309. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48574-w. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38830846 Free PMC article.
-
CTLA4-Ig in combination with FTY720 promotes allograft survival in sensitized recipients.JCI Insight. 2017 May 4;2(9):e92033. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.92033. eCollection 2017 May 4. JCI Insight. 2017. PMID: 28469082 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-CD28 Antibody and Belatacept Exert Differential Effects on Mechanisms of Renal Allograft Rejection.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016 Dec;27(12):3577-3588. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2015070774. Epub 2016 May 9. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27160407 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sallusto F, Lanzavecchia A. Heterogeneity of CD4+ memory T cells: functional modules for tailored immunity. Eur J Immunol. 2009;39:2076–2082. - PubMed
-
- Zielinski CE, Corti D, Mele F, Pinto D, Lanzavecchia A, Sallusto F. Dissecting the human immunologic memory for pathogens. Immunol Rev. 2011;240:40–51. - PubMed
-
- Smith C, Miles JJ, Khanna R. Advances in direct T-cell alloreactivity: function, avidity, biophysics and structure. Am J Transplant. 2012;12:15–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

