Evaluation of biophysical skin parameters and assessment of hair growth in patients with acne treated with isotretinoin
- PMID: 24493996
- PMCID: PMC3907898
- DOI: 10.5114/pdia.2013.39432
Evaluation of biophysical skin parameters and assessment of hair growth in patients with acne treated with isotretinoin
Abstract
Introduction: Treatment of the severe forms of acne vulgaris remains a challenge. Isotretinoin is a drug often used in these cases. Retinoids affect the mechanisms that play a role in the pathogenesis of acne, reduce the production of sebum and sizes of the sebaceous glands. However, isotretinoin appears to have undesirable side effects in the skin, mucous membranes and hair.
Aim: THE AIM OF THIS STUDY WAS TO ASSESS THE EFFECT OF ACNE VULGARIS TREATMENT WITH ISOTRETINOIN ON BIOPHYSICAL SKIN PARAMETERS: skin sebum and stratum corneum hydration levels, transepidermal water loss values, pH, erythema and hair growth parameters: total number, density and proportion of anagen hair.
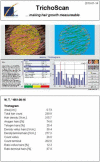
Material and methods: THE STUDY INCLUDED THIRTY PATIENTS WITH ACNE TYPES: papulopustular, conglobata and phlegmonosa. Patients were treated with isotretinoin at a dose of 0.5-1.0 mg/kg/day for a period of 4-7 months. The measurements of skin biophysical parameters were performed before and after the treatment using Sebumeter SM815, Corneometer CM825, Tewameter TM300, MX Mexameter MX18 and Skin-pH-Meter PH908. Hair growth parameters were evaluated with FotoFinder Dermoscope using the TrichoScan Professional V3.0.8.76 software.
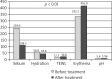
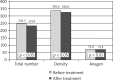
Results: The results of biophysical skin parameter measurements after the treatment showed a reduction in the severity of seborrhea. However, the skin was dry, which confirmed a lowered degree of stratum corneum hydration and an increase in transepidermal water loss values. Moreover, severity of erythema, an increase in pH value, and variations in selected hair growth parameters: decrease in total count, density and proportion of anagen hair were demonstrated.
Conclusions: The reduction in the skin sebum levels was observed after the treatment. There was dryness of the skin, which was confirmed by biophysical skin parameter measurements. Changes in the hair growth parameters showed telogen effluvium hair loss.
Keywords: acne vulgaris; biophysical skin parameters; isotretinoin; trichoscan.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The effect of systemic isotretinoin treatment on skin biophysicalparameters among patients with acne vulgaris.Turk J Med Sci. 2016 Dec 20;46(6):1641-1644. doi: 10.3906/sag-1507-31. Turk J Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 28081350
-
Evaluation of biophysical skin parameters and hair changes in patients with acne vulgaris treated with isotretinoin, and the effect of biotin use on these parameters.Int J Dermatol. 2021 Aug;60(8):980-985. doi: 10.1111/ijd.15485. Epub 2021 Mar 8. Int J Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 33682085
-
Effects of isotretinoin on the hair cycle.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2019 Apr;18(2):647-651. doi: 10.1111/jocd.12800. Epub 2018 Oct 23. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 30350907 Clinical Trial.
-
Role of Oral Retinoids in Treatment of Acne Vulgaris With a Bioinformatics-Based Perspective of Personalized Medicine.Cureus. 2023 Apr 23;15(4):e38019. doi: 10.7759/cureus.38019. eCollection 2023 Apr. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37228537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral isotretinoin for acne.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Nov 24;11(11):CD009435. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009435.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30484286 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Changes in hair cortisol concentration in intrauterine device initiators: A prospective cohort study.Contraception. 2023 Dec;128:110142. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2023.110142. Epub 2023 Aug 24. Contraception. 2023. PMID: 37633589 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative and Mechanistic Approach to the Hair Growth Cycle and Hair Loss.J Clin Med. 2023 Jan 23;12(3):893. doi: 10.3390/jcm12030893. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36769541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reduction in Facial Sebum Production Following Treatment with Clascoterone Cream 1% in Patients with Acne Vulgaris: 12-Week Interim Analysis.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2025 Sep;15(9):2657-2666. doi: 10.1007/s13555-025-01495-y. Epub 2025 Jul 19. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2025. PMID: 40682762 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Evening Primrose Oil Supplementation on Selected Parameters of Skin Condition in a Group of Patients Treated with Isotretinoin-A Randomized Double-Blind Trial.Nutrients. 2022 Jul 21;14(14):2980. doi: 10.3390/nu14142980. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35889936 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The influence of selected ingredients of dietary supplements on skin condition.Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2014 Jun;31(3):174-81. doi: 10.5114/pdia.2014.40919. Epub 2014 Jun 13. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2014. PMID: 25097490 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Titus S, Hodge J. Diagnosis and treatment of acne. Am Fam Physician. 2012;86:734–40. - PubMed
-
- Tałasiewicz K, Ołdakowska A, Szczerkowska-Dobosz A. Evaluation of knowledge about acne vulgaris among a selected population of adolescents of Tricity schools. Postep Derm Alergol. 2012;296:417–20.
-
- Brzezińska-Wcisło L, Bergler-Czop B, Wcisło-Dziadecka D, Lis-Święty A. What's new in pathogenesis of acne [Polish] Dermatol Klin. 2006;8:275–9.
-
- Silny W, Bartoszak L, Jenerowicz D, et al. Prevalence of contact allergy in children suffering from atopic dermatitis, seborrhoeic dermatitis and in healthy controls. Ann Agric Environ Med. 2013;20:55–60. - PubMed
-
- Williams HC, Dellavalle RP, Garner S. Acne vulgaris. Lancet. 2012;379:361–72. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
