Acute warfarin toxicity: An unanticipated consequence of amoxicillin/clavulanate administration
- PMID: 24494060
- PMCID: PMC3908910
- DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.889866
Acute warfarin toxicity: An unanticipated consequence of amoxicillin/clavulanate administration
Abstract
Patient: Male, 53 FINAL DIAGNOSIS: Acute Warfarin toxicity Symptoms: -
Medication: Warfarin Clinical Procedure: - Specialty: Hematology.
Objective: Unusual clinical course.
Background: Warfarin remains the most common anticoagulant in the management of thromboembolic diseases. However, its extensive drug interaction requires frequent monitoring and dose adjustments. Almost all antibiotics, including penicillins, have the potential to interact with warfarin causing either under or over anticoagulation which increases the risk for thrombus formation and significant bleeding respectively.
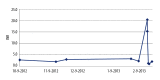
Case report: A 53-year-old Caucasian male with a history of protein C deficiency and recurrent intravascular thrombosis developed a dental abscess. He was treated with amoxicillin/clavulanate 500/125 mg twice daily and referred to a dentist. He developed significant bleeding after tooth extraction. INR was 20.4. He received fresh frozen plasma and vitamin K with resolution of bleeding.
Conclusions: While rare, clinically significant prolonged prothrombin time and potentially life threatening bleeding can occur when amoxicillin/clavulanate is concomitantly administered with warfarin. Prompt recognition and intervention is necessary to avoid life threatening complications from warfarin-amoxicillin/clavulanate interaction.
Keywords: Amoxicillin; Clavulanic Acid; Protein C Deficiency; Warfarin – adverse effects; supratherapeutic INR.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Warfarin-drug interactions: An emphasis on influence of polypharmacy and high doses of amoxicillin/clavulanate.J Clin Pharmacol. 2016 Jan;56(1):39-46. doi: 10.1002/jcph.583. Epub 2015 Sep 29. J Clin Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26138877
-
Formation of rectus sheath hematoma with antibiotic use and warfarin therapy: a case report.Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2005 Dec;3(4):266-9. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2005. PMID: 16503323
-
Warfarin and amoxicillin/clavulanate drug interaction.Ann Pharmacother. 2003 Mar;37(3):367-70. doi: 10.1345/aph.1C243. Ann Pharmacother. 2003. PMID: 12639164
-
The use of vitamin K in patients on anticoagulant therapy: a practical guide.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2004;4(1):43-55. doi: 10.2165/00129784-200404010-00005. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2004. PMID: 14967065 Review.
-
A clinically significant drug interaction between warfarin and amoxicillin resulting in persistent postoperative bleeding in a dental patient.Gen Dent. 2013 Jul;61(4):50-4. Gen Dent. 2013. PMID: 23823345 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of VKORC1 Genetic Polymorphisms on Warfarin Maintenance Dose Requirement in a Chinese Han Population.Med Sci Monit. 2015 Nov 19;21:3577-84. doi: 10.12659/msm.894414. Med Sci Monit. 2015. PMID: 26583785 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jacobs LG. Warfarin pharmacology, clinical management, and evaluation of hemorrhagic risk for the elderly. Clin Geriatr Med. 2005;22:17–32. - PubMed
-
- Holbrook AM, Pereira JA, Labiris R, et al. Systematic overview of warfarin and its drug and food interactions. Arch Intern Med. 2005;165:1095–106. - PubMed
-
- Penning-van Beest F, Erkens J, Petersen KU, et al. Main comedications associated with major bleeding during anticoagulant therapy with coumarins. Eur J ClinPharmacol. 2005;61:439–44. - PubMed
-
- Freedman MD, Olatidoye AG. Clinically significant drug interactions with the oral anticoagulants. Drug Safety. 1994;10(5):381–94. - PubMed
-
- Freedman MD. Oral anticoagulants: pharmacodynamics, clinical indications and adverse effects. J Clin Pharmacol. 1992;32(3):196–209. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources