The neurobiology of skeletal pain
- PMID: 24494689
- PMCID: PMC4453827
- DOI: 10.1111/ejn.12462
The neurobiology of skeletal pain
Abstract
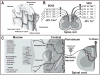
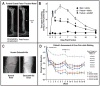
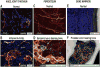
Disorders of the skeleton are one of the most common causes of chronic pain and long-term physical disability in the world. Chronic skeletal pain is caused by a remarkably diverse group of conditions including trauma-induced fracture, osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, low back pain, orthopedic procedures, celiac disease, sickle cell disease and bone cancer. While these disorders are diverse, what they share in common is that when chronic skeletal pain occurs in these disorders, there are currently few therapies that can fully control the pain without significant unwanted side effects. In this review we focus on recent advances in our knowledge concerning the unique population of primary afferent sensory nerve fibers that innervate the skeleton, the nociceptive and neuropathic mechanisms that are involved in driving skeletal pain, and the neurochemical and structural changes that can occur in sensory and sympathetic nerve fibers and the CNS in chronic skeletal pain. We also discuss therapies targeting nerve growth factor or sclerostin for treating skeletal pain. These therapies have provided unique insight into the factors that drive skeletal pain and the structural decline that occurs in the aging skeleton. We conclude by discussing how these advances have changed our understanding and potentially the therapeutic options for treating and/or preventing chronic pain in the injured, diseased and aged skeleton.
Keywords: CRPS; age; bone; cartilage; marrow; nociceptor.
Published 2014. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA.
Figures


References
-
- Albrecht PJ, Hines S, Eisenberg E, Pud D, Finlay DR, Connolly MK, Pare M, Davar G, Rice FL. Pathologic alterations of cutaneous innervation and vasculature in affected limbs from patients with complex regional pain syndrome. Pain. 2006;120:244–266. - PubMed
-
- Albrecht PJ, Rice FL. Role of small-fiber afferents in pain mechanisms with implications on diagnosis and treatment. Current pain and headache reports. 2010;14:179–188. - PubMed
-
- Aoki Y, Ohtori S, Takahashi K, Ino H, Douya H, Ozawa T, Saito T, Moriya H. Expression and co-expression of VR1, CGRP, and IB4-binding glycoprotein in dorsal root ganglion neurons in rats: differences between the disc afferents and the cutaneous afferents. Spine. 2005;30:1496–1500. - PubMed
-
- Archer CW, Williams R, Nelson L, Khan IM. Articular Cartilage-Derived Stem Cells: Identification, Characterisation and their Role in Spontaneous Repair. Rheumatology: Current Research 2012
-
- Artico M, Bronzetti E, Felici LM, Alicino V, Ionta B, Bronzetti B, Magliulo G, Grande C, Zamai L, Pasquantonio G, De Vincentiis M. Neurotrophins and their receptors in human lingual tonsil: an immunohistochemical analysis. Oncology reports. 2008;20:1201–1206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

