A double-blind, randomized clinical trial of dietary supplementation on cognitive and immune functioning in healthy older adults
- PMID: 24495355
- PMCID: PMC3916807
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-43
A double-blind, randomized clinical trial of dietary supplementation on cognitive and immune functioning in healthy older adults
Erratum in
- BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014;14:332
Abstract
Background: Declining cognitive function is relatively common and increasingly prevalent. Studies have shown that different nutrients (e.g., Ginkgo biloba and vitamin E) appear to be effective at improving memory and concentration, while less is known about their effect on immunity.
Methods: This study investigated the effect of Ginkgo Synergy(®) plus Choline (n = 33) and OPC Synergy(®) plus Catalyn(®) (n = 31) versus placebo (n = 33) in a 6-month, randomized, double-blind trial on cognitive and immune functioning among English-speaking, non-smoking, healthy older adults. The Stroop Color and Word Test, Trail Making Test A and B, Controlled Oral Word Association, Hopkins Verbal Learning, Mini-Mental State Exam, and Digit Symbol were administered at baseline and 3 and 6 months follow-up to assess cognitive functioning. Cytokines and growth factors were measured at baseline and 6 months to assess inflammation and immune functioning. Data were analyzed with linear mixed modeling.
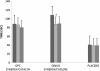
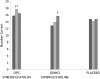
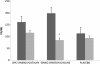
Results: No serious adverse events were noted in this study. According to time on the Trail Making Test-B, the Ginkgo Synergy(®) plus Choline arm showed improvement from baseline to 3 months follow-up (mean difference = 24.2; SE = 6.4; 95% CI: 8.6, 39.7; p = 0.01). On the Controlled Oral Word Association Trial-S, the scores significantly increased for the Ginkgo Synergy(®) plus Choline arm from baseline to 6 months follow-up (mean difference = 2.1; SE = 0.8; 95% CI: 0.2, 3.9; p < 0.05) and for the OPC Synergy(®) plus Catalyn(®) arm from baseline to 3 months follow-up (mean difference = 2.1; SE = 0.8; 95% CI: 0.2, 4.0; p < 0.05). Epidermal growth factor significantly decreased from baseline to 6 months follow-up for the Ginkgo Synergy(®) plus Choline arm (mean difference = 120.7; SE = 28.4; 95% CI: 62.6, 178.8; p < 0.001).
Conclusions: Our study showed isolated and modest effects of a Ginkgo biloba plus choline-based formula on cognitive and immune functioning among healthy older adults with no history of significant cognitive deficits. Our trial was registered with clinicaltrials.gov (ID: NCT01672359). This study was supported by a grant from Standard Process, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Beers MH, Berkow R. The Merck Manual of Geriatrics. Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck Research Laboratories; 2000.
-
- Association A's. Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2012;2012(8):131–168. - PubMed
-
- Nutrition Business Journal. Nutrition Business Journal Supplement Business Report 2010. Cleveland, OH: Pendon Media, Inc.; 2010.
-
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III: Use of Dietary Supplements. http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhanes/databriefs/dietary.pdf.
-
- Winslow LC, Kroll DJ. Herbs as medicines. Arch Intern Med. 1998;158:2192–2199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

