Accounting for cellular heterogeneity is critical in epigenome-wide association studies
- PMID: 24495553
- PMCID: PMC4053810
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2014-15-2-r31
Accounting for cellular heterogeneity is critical in epigenome-wide association studies
Abstract
Background: Epigenome-wide association studies of human disease and other quantitative traits are becoming increasingly common. A series of papers reporting age-related changes in DNA methylation profiles in peripheral blood have already been published. However, blood is a heterogeneous collection of different cell types, each with a very different DNA methylation profile.
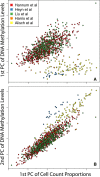
Results: Using a statistical method that permits estimating the relative proportion of cell types from DNA methylation profiles, we examine data from five previously published studies, and find strong evidence of cell composition change across age in blood. We also demonstrate that, in these studies, cellular composition explains much of the observed variability in DNA methylation. Furthermore, we find high levels of confounding between age-related variability and cellular composition at the CpG level.
Conclusions: Our findings underscore the importance of considering cell composition variability in epigenetic studies based on whole blood and other heterogeneous tissue sources. We also provide software for estimating and exploring this composition confounding for the Illumina 450k microarray.
Figures



References
-
- Rakyan VK, Beyan H, Down TA, Hawa MI, Maslau S, Aden D, Daunay A, Busato F, Mein CA, Manfras B, Dias KR, Bell CG, Tost J, Boehm BO, Beck S, Leslie RD. Identification of type 1 diabetes-associated DNA methylation variable positions that precede disease diagnosis. PLoS Genet. 2011;7:e1002300. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Aryee MJ, Padyukov L, Fallin MD, Hesselberg E, Runarsson A, Reinius L, Acevedo N, Taub M, Ronninger M, Shchetynsky K, Scheynius A, Kere J, Alfredsson L, Klareskog L, Ekstrom TJ, Feinberg AP. Epigenome-wide association data implicate DNA methylation as an intermediary of genetic risk in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Biotechnol. 2013;31:142–147. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

