Synaptic tagging during memory allocation
- PMID: 24496410
- PMCID: PMC3992944
- DOI: 10.1038/nrn3667
Synaptic tagging during memory allocation
Abstract
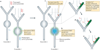
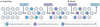
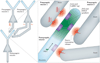
There is now compelling evidence that the allocation of memory to specific neurons (neuronal allocation) and synapses (synaptic allocation) in a neurocircuit is not random and that instead specific mechanisms, such as increases in neuronal excitability and synaptic tagging and capture, determine the exact sites where memories are stored. We propose an integrated view of these processes, such that neuronal allocation, synaptic tagging and capture, spine clustering and metaplasticity reflect related aspects of memory allocation mechanisms. Importantly, the properties of these mechanisms suggest a set of rules that profoundly affect how memories are stored and recalled.
Figures
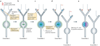
References
-
- Eichenbaum H. A cortical–hippocampal system for declarative memory. Nature Rev. Neurosci. 2000;1:41–50. - PubMed
-
- Nader K, et al. The labile nature of consolidation theory. Nature Rev. Neurosci. 2000;1:216–219. - PubMed
-
- Schafe GE, et al. Memory consolidation of Pavlovian fear conditioning: a cellular and molecular perspective. Trends Neurosci. 2001;24:540–546. - PubMed
-
- Bouton ME. Context and behavioral processes in extinction. Learn. Mem. 2004;11:485–494. - PubMed
-
- Maren S, Quirk GJ. Neuronal signalling of fear memory. Nature Rev. Neurosci. 2004;5:844–852. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

