Proteomic profiling of cardiac tissue by isolation of nuclei tagged in specific cell types (INTACT)
- PMID: 24496632
- PMCID: PMC3912835
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.098327
Proteomic profiling of cardiac tissue by isolation of nuclei tagged in specific cell types (INTACT)
Abstract
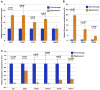
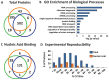
The proper dissection of the molecular mechanisms governing the specification and differentiation of specific cell types requires isolation of pure cell populations from heterogeneous tissues and whole organisms. Here, we describe a method for purification of nuclei from defined cell or tissue types in vertebrate embryos using INTACT (isolation of nuclei tagged in specific cell types). This method, previously developed in plants, flies and worms, utilizes in vivo tagging of the nuclear envelope with biotin and the subsequent affinity purification of the labeled nuclei. In this study we successfully purified nuclei of cardiac and skeletal muscle from Xenopus using this strategy. We went on to demonstrate the utility of this approach by coupling the INTACT approach with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) proteomic methodologies to profile proteins expressed in the nuclei of developing hearts. From these studies we have identified the Xenopus orthologs of 12 human proteins encoded by genes, which when mutated in human lead to congenital heart disease. Thus, by combining these technologies we are able to identify tissue-specific proteins that are expressed and required for normal vertebrate organ development.
Keywords: Cardiac muscle; INTACT; Proteomics; Skeletal muscle; Xenopus.
Figures
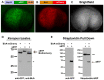
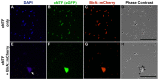
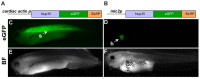
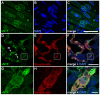
References
-
- Afouda B. A., Hoppler S. (2009). Xenopus explants as an experimental model system for studying heart development. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 19, 220–226 - PubMed
-
- Agostini M., Tucci P., Killick R., Candi E., Sayan B. S., Rivetti di Val Cervo P., Nicotera P., McKeon F., Knight R. A., Mak T. W., et al. (2011). Neuronal differentiation by TAp73 is mediated by microRNA-34a regulation of synaptic protein targets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108, 21093–21098 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al-Saaidi R., Rasmussen T. B., Palmfeldt J., Nissen P. H., Beqqali A., Hansen J., Pinto Y. M., Boesen T., Mogensen J., Bross P. (2013). The LMNA mutation p.Arg321Ter associated with dilated cardiomyopathy leads to reduced expression and a skewed ratio of lamin A and lamin C proteins. Exp. Cell Res. 319, 3010–3019 - PubMed
-
- Amaya E., Kroll K. L. (1999). A method for generating transgenic frog embryos. Methods Mol. Biol. 97, 393–414 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

