White matter disease as a biomarker for long-term cerebrovascular disease and dementia
- PMID: 24496967
- PMCID: PMC3964019
- DOI: 10.1007/s11936-013-0292-z
White matter disease as a biomarker for long-term cerebrovascular disease and dementia
Abstract
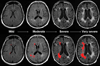
White matter disease is commonly detected on brain MRI of aging individuals as white matter hyperintensities (WMH), or 'leukoaraiosis." Over the years, it has become increasingly clear that the presence and extent of WMH is a radiographic marker of small cerebral vessel disease and an important predictor of the lifelong risk of stroke, cognitive impairment, and functional disability. A number of large population-based studies have outlined the significance of WMH as a biomarker for long-term cerebrovascular disease and dementia. In this review, we describe the conceptual framework and methodology that support this association and link the existing knowledge to future lines of investigation in the field.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Chutinet reports no disclosure.
Figures
References
-
-
Sacco RL, Kasner SE, Broderick JP, et al. An updated definition of stroke for the 21st century: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2013;44:2064–2089. This expert consensus statement provides the most updated evidence in support of the new definition of stroke.
-
-
- Hachinski VC, Potter P, Merskey H. Leuko-araiosis: an ancient term for a new problem. Can J Neurol Sci. 1986;13(4 Suppl):533–534. - PubMed
-
- Hachinski VC, Potter P, Merskey H. Leuko-araiosis. Arch Neurol. 1987;44:21–23. - PubMed
-
- Fazekas F, Barkhof F, Wahlund LO, et al. CT and MRI rating of white matter lesions. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2002;13(Suppl 2):31–36. - PubMed
-
- Fazekas F, Chawluk JB, Alavi A, et al. MR signal abnormalities at 1.5 T in Alzheimer's dementia and normal aging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987;149:351–356. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

