The transcript elongation factor SPT4/SPT5 is involved in auxin-related gene expression in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 24497194
- PMCID: PMC3985667
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gku096
The transcript elongation factor SPT4/SPT5 is involved in auxin-related gene expression in Arabidopsis
Abstract
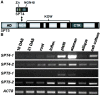
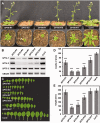
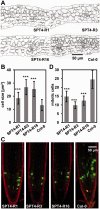
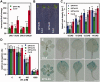
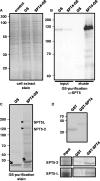
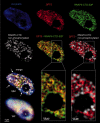
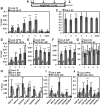
The heterodimeric complex SPT4/SPT5 is a transcript elongation factor (TEF) that directly interacts with RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) to regulate messenger RNA synthesis in the chromatin context. We provide biochemical evidence that in Arabidopsis, SPT4 occurs in a complex with SPT5, demonstrating that the SPT4/SPT5 complex is conserved in plants. Each subunit is encoded by two genes SPT4-1/2 and SPT5-1/2. A mutant affected in the tissue-specifically expressed SPT5-1 is viable, whereas inactivation of the generally expressed SPT5-2 is homozygous lethal. RNAi-mediated downregulation of SPT4 decreases cell proliferation and causes growth reduction and developmental defects. These plants display especially auxin signalling phenotypes. Consistently, auxin-related genes, most strikingly AUX/IAA genes, are downregulated in SPT4-RNAi plants that exhibit an enhanced auxin response. In Arabidopsis nuclei, SPT5 clearly localizes to the transcriptionally active euchromatin, and essentially co-localizes with transcribing RNAPII. Typical for TEFs, SPT5 is found over the entire transcription unit of RNAPII-transcribed genes. In SPT4-RNAi plants, elevated levels of RNAPII and SPT5 are detected within transcribed regions (including those of downregulated genes), indicating transcript elongation defects in these plants. Therefore, SPT4/SPT5 acts as a TEF in Arabidopsis, regulating transcription during the elongation stage with particular impact on the expression of certain auxin-related genes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Elongator and SPT4/SPT5 complexes as proxy to study RNA polymerase II transcript elongation control of plant development.Proteomics. 2014 Oct;14(19):2109-14. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201400024. Epub 2014 May 22. Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 24733746
-
Biochemical Analysis of Yeast Suppressor of Ty 4/5 (Spt4/5) Reveals the Importance of Nucleic Acid Interactions in the Prevention of RNA Polymerase II Arrest.J Biol Chem. 2016 May 6;291(19):9853-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.716001. Epub 2016 Mar 4. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26945063 Free PMC article.
-
Different elongation factors distinctly modulate RNA polymerase II transcription in Arabidopsis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Nov 27;51(21):11518-11533. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad825. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37819035 Free PMC article.
-
Transcript elongation by RNA polymerase II in plants: factors, regulation and impact on gene expression.Plant J. 2024 May;118(3):645-656. doi: 10.1111/tpj.16115. Epub 2023 Feb 12. Plant J. 2024. PMID: 36703573 Review.
-
The Spt4-Spt5 complex: a multi-faceted regulator of transcription elongation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jan;1829(1):105-15. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.08.007. Epub 2012 Sep 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 22982195 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic and signalling pathways of dry fruit size: targets for genome editing-based crop improvement.Plant Biotechnol J. 2020 May;18(5):1124-1140. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13318. Epub 2020 Jan 25. Plant Biotechnol J. 2020. PMID: 31850661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant chromatin warms up in Madrid: meeting summary of the 3rd European Workshop on Plant Chromatin 2013, Madrid, Spain.Epigenetics. 2014 Apr;9(4):644-52. doi: 10.4161/epi.28094. Epub 2014 Feb 6. Epigenetics. 2014. PMID: 24504145 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct role of subunits of the Arabidopsis RNA polymerase II elongation factor PAF1C in transcriptional reprogramming.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Sep 29;13:974625. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.974625. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36247629 Free PMC article.
-
Plant growth promotion by the interaction of a novel synthetic small molecule with GA-DELLA function.Plant Direct. 2022 Apr 26;6(4):e398. doi: 10.1002/pld3.398. eCollection 2022 Apr. Plant Direct. 2022. PMID: 35492684 Free PMC article.
-
The Arabidopsis THO/TREX component TEX1 functionally interacts with MOS11 and modulates mRNA export and alternative splicing events.Plant Mol Biol. 2017 Feb;93(3):283-298. doi: 10.1007/s11103-016-0561-9. Epub 2016 Dec 21. Plant Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28004241
References
-
- Saunders A, Core LJ, Lis JT. Breaking barriers to transcription elongation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006;7:557–567. - PubMed
-
- Selth LA, Sigurdsson S, Svejstrup JQ. Transcript elongation by RNA Polymerase II. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 2010;79:271–293. - PubMed
-
- Sims RJ, Belotserkovskaya R, Reinberg D. Elongation by RNA polymerase II: the short and the long of it. Genes Dev. 2004;18:2437–2468. - PubMed
-
- Grasser KD. Emerging role for transcript elongation in plant development. Trends Plant Sci. 2005;10:484–490. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

