Update on treatment of light chain amyloidosis
- PMID: 24497558
- PMCID: PMC3912950
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2013.087619
Update on treatment of light chain amyloidosis
Abstract
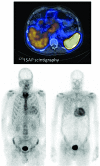
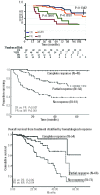
Light chain amyloidosis is the most common type of amyloidosis as a consequence of protein misfolding of aggregates composed of amyloid fibrils. The clinical features are dependent on the organs involved, typically cardiac, renal, hepatic, peripheral and autonomic neuropathy and soft tissue. A tissue biopsy or fat aspirate is needed to confirm the presence/type of amyloid and prognostic tools are important in a risk stratified approach to treatment. Autologous stem cell transplant eligibility should be assessed at baseline, weighing the reversible or non-reversible contraindications, toxicity of treatment and chemotherapy alternatives available. Chemotherapy options include melphalan, thalidomide, bortezomib, lenalidomide, bendamustine in combination with dexamethasone. Many studies have explored these treatment modalities, with ongoing debate about the optimal first line and sequential treatment thereafter. Attaining a very good partial response or better is the treatment goal coupled with early assessment central to optimizing treatment. One major challenge remains increasing the awareness of this disease, frequently diagnosed late as the presenting symptoms mimic many other medical conditions. This review focuses on the treatments for light chain amyloidosis, how these treatments have evolved over the years, improved patient risk stratification, toxicities encountered and future directions.
Figures



References
-
- Kyle RA, Gertz MA. Primary systemic amyloidosis: clinical and laboratory features in 474 cases. Semin Hematol. 1995;32(1):45–59 - PubMed
-
- Sipe JD, Benson MD, Buxbaum JN, Ikeda SI, Merlini G, Saraiva MJ, et al. Amyloid fibril protein nomenclature: 2012 recommendations from the Nomenclature Committee of the International Society of Amyloidosis. Amyloid. 2012;19(4):167–70 - PubMed
-
- Weiss BM, Hebreo J, Cordaro D, Roschewski MJ, Abbott KC, Olson SW. Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) precedes the diagnosis of AL amyloidosis by up to 14 years. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts). 2011;118:1827
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

