Dialysis adequacy indices and body composition in male and female patients on peritoneal dialysis
- PMID: 24497588
- PMCID: PMC4079488
- DOI: 10.3747/pdi.2013.00018
Dialysis adequacy indices and body composition in male and female patients on peritoneal dialysis
Abstract
Objectives: Creatinine clearance scaled to body surface area (BSA) and urea KT/V normalized to total body water (TBW) are used as indices for peritoneal dialysis (PD) adequacy. We investigated relationships of indices of dialysis adequacy (including KT/V, KT, clearance, dialysate over plasma concentration ratio) and anthropometric and body composition parameters (BSA, TBW, body mass index (BMI), weight, height, fat mass (FM), and fat-free mass (FFM)) in male and female patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis.
Methods: Ninety-nine stable patients (56 males) performed four 24-hr collections of drained dialysate for four dialysis schedules with three daily exchanges of glucose 1.36% and one night exchange of either: 1) glucose 1.36%, 2) glucose 2.27%, 3) glucose 3.86% or 4) icodextrin 7.5%.
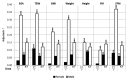
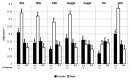
Results: KT and dialysate over plasma concentration ratio, CD/CP, for urea and creatinine were similar for males and females and, in general, did not depend on body-size parameters including V (= TBW), which means that the overall capacity of the transport system in females and males is similar. However, after normalization of KT to V or 1.73/BSA yielding KT/V and creatinine clearance, Cl(1.73/BSA), respectively, the normalized indices were substantially higher in females than in males and correlated inversely with body-size parameters, especially in males.
Conclusions: As KT/V depends strongly on body size, treatment target values for KT/V should take body size and therefore also gender into account. As KT is less influenced by body size, body composition and gender, KT should be considered as a potential auxiliary index in PD.
Keywords: KT/V; Peritoneal dialysis adequacy; body composition; clearance; creatinine; gender; urea.
Copyright © 2014 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of Alternative Approaches to Normalizing Peritoneal Dialysis Clearance with Mortality and Technique Failure: A Retrospective Analysis Using the United States Renal Data System-Dialysis Morbidity and Mortality Study, Wave 2.Perit Dial Int. 2017 1-2;37(1):85-93. doi: 10.3747/pdi.2015.00227. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Perit Dial Int. 2017. PMID: 27680757 Free PMC article.
-
The relation between body size and normalized small solute clearances in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis.J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999 Jul;10(7):1575-81. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V1071575. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999. PMID: 10405214
-
[The effect of recombinant human growth hormone on urea and creatinine kinetics and selected dialysis adequacy parameters in children with end-stage renal failure treated with peritoneal dialysis].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2002 Sep;13(75):191-5. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2002. PMID: 12474568 Polish.
-
The prescription of peritoneal dialysis.Semin Dial. 2008 May-Jun;21(3):250-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-139X.2007.00412.x. Epub 2008 Feb 1. Semin Dial. 2008. PMID: 18248525 Review.
-
How should we measure peritoneal dialysis adequacy in the clinic.Contrib Nephrol. 2009;163:140-146. doi: 10.1159/000223792. Epub 2009 Jun 3. Contrib Nephrol. 2009. PMID: 19494607 Review.
Cited by
-
Normalized Protein Catabolic Rate Is a Superior Nutritional Marker Associated With Dialysis Adequacy in Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis Patients.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Jan 12;7:603725. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.603725. eCollection 2020. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33511142 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Affecting Hemodialysis Adequacy in Cohort of Iranian Patient with End Stage Renal Disease.Glob J Health Sci. 2016 Aug 1;8(8):55781. doi: 10.5539/gjhs.v8n8p50. Glob J Health Sci. 2016. PMID: 27045416 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of gender and dialysis adequacy on anaemia in peritoneal dialysis.Int Urol Nephrol. 2017 May;49(5):903-908. doi: 10.1007/s11255-016-1499-1. Epub 2017 Jan 5. Int Urol Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28058668 Free PMC article.
-
Single-pool model urea clearance index is associated with sarcopenia and nutritional status in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis: a cross-sectional study.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Mar 5;25(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03510-4. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38443824 Free PMC article.
-
Sex difference in the association among nutrition, muscle mass, and strength in peritoneal dialysis patients.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 25;12(1):17900. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22722-y. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36284230 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Twardowski ZJ, Moore HL, Prowant BF, Satalowich R. Long-term follow-up of body size indices, residual renal function, and peritoneal transport characteristics in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Adv Perit Dial 2009; 25:155–64 - PubMed
-
- Tzamaloukas AH, Murata GH, Piraino B, Malhotra D, Bernardini J, Rao P, et al. The relation between body size and normalized small solute clearances in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol 1999; 10(7):1575–81 - PubMed
-
- Rocco MV, Frankenfield DL, Prowant B, Frederick P, Flanigan MJ. Risk factors for early mortality in U.S. peritoneal dialysis patients: Impact of residual renal function. Perit Dial Int 2002; 22(3):371–9 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

