Deoxyribonucleic acid repair gene X-ray repair cross-complementing group 1 polymorphisms and non-carcinogenic disease risk in different populations: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 24497722
- PMCID: PMC3897152
- DOI: 10.4103/0971-6866.124385
Deoxyribonucleic acid repair gene X-ray repair cross-complementing group 1 polymorphisms and non-carcinogenic disease risk in different populations: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: This study aims to assess a meta-analysis of the association of X-ray repair cross-complementing group 1 (XRCC1) polymorphisms with the risk of various non-carcinogenic diseases in different population.
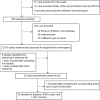
Materials and methods: This meta-analysis was performed by critically reviewing reveals 38 studies involving 10043 cases and 11037 controls. Among all the eligible studies, 14 focused on Arg194Trp polymorphism, 33 described the Arg399Gln and three articles investigated on Arg280His. Populations were divided into three different ethnic subgroups include Caucasians, Asians and other (Turkish and Iranian).
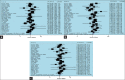
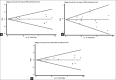
Results: Pooled results showed no correlation between Arg194Trp and non-carcinogenic disease. There was only weak relation in the recessive (odds ratio [OR] =1.11, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.86-1.44) model in Asian population and dominant (OR = 1.04, 95% CI: 0.66-1.63) model of other populations. In Arg399Gln polymorphism, there was no relation with diseases of interest generally. In the pooled analysis, there were weak relation in the dominant (OR = 1.08, 95% CI: 0.86-1.35) model of Asian population and quite well-correlation with recessive (OR = 1.49, 95% CI: 1.19-1.88), dominant (OR = 1.23, 95% CI: 0.94-1.62), and additive (OR = 1.23, 95% CI: 0.94-1.62) models of other subgroup. For Arg280His, there was a weak relation only in the dominant model (OR = 1.06, 95% CI: 0.74-1.51).
Conclusion: The present meta-analysis correspondingly shows that Arg399Gln variant to be associated with increased non-carcinogenic diseases risk through dominant and recessive modes among Iranian and Turkish population. It also suggests a trend of dominant and recessive effect of Arg280His variant in all population and its possible protective effect on non-carcinogenic diseases.
Keywords: Arg194Trp; Arg280His; Arg399Gln; X-ray repair cross-complementing group 1 gene; ethnicity; non-carcinogenic diseases; polymorphisms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures









Similar articles
-
Association between the XRCC1 polymorphisms and glioma risk: a meta-analysis of case-control studies.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e55597. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055597. Epub 2013 Jan 30. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23383237 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between X-ray cross-complementing group 1 polymorphisms and the onset risk of glioma: A meta-analysis.Neural Regen Res. 2013 Sep 15;8(26):2468-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2013.26.008. Neural Regen Res. 2013. PMID: 25206557 Free PMC article.
-
Association of X-ray repair cross-complementing group 1 Arg194Trp, Arg399Gln and Arg280His polymorphisms with head and neck cancer susceptibility: a meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 30;9(1):e86798. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086798. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24497981 Free PMC article.
-
X-ray repair cross-complementing group 1 polymorphisms and hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Aug 21;18(31):4207-14. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i31.4207. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22919255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
No association between XRCC1 genetic polymorphisms and differentiated thyroid carcinoma risk: a meta-analysis.Mol Biol Rep. 2014 Nov;41(11):7613-21. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3651-2. Epub 2014 Aug 3. Mol Biol Rep. 2014. PMID: 25086624
Cited by
-
Innumerable studies on single nucleotide polymorphisms: What could be its utility?Indian J Hum Genet. 2013 Oct;19(4):381-3. doi: 10.4103/0971-6866.124354. Indian J Hum Genet. 2013. PMID: 24497699 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Okayasu R. Repair of DNA damage induced by accelerated heavy ions - A mini review. Int J Cancer. 2012;130:991–1000. - PubMed
-
- Shen MR, Jones IM, Mohrenweiser H. Nonconservative amino acid substitution variants exist at polymorphic frequency in DNA repair genes in healthy humans. Cancer Res. 1998;58:604–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

