Terminology and reporting criteria for radiofrequency ablation of tumors in the scientific literature: systematic review of compliance with reporting standards
- PMID: 24497798
- PMCID: PMC3909868
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2014.15.1.95
Terminology and reporting criteria for radiofrequency ablation of tumors in the scientific literature: systematic review of compliance with reporting standards
Abstract
Objective: To perform a systematic review of compliance with standardized terminology and reporting criteria for radiofrequency (RF) tumor ablation, proposed by the International Working Group on Image-Guided Tumor Ablation in 2003, in the published reports.
Materials and methods: Literature search in the PubMed database was performed using index keywords, PubMed limit system, and eligibility criteria. The entire content of each article was reviewed to assess the terminology used for procedure terms, imaging findings, therapeutic efficacy, follow-up, and complications. Accuracy of the terminology and the use of alternative terms instead of standard terminology were analyzed. In addition, disparities in accuracy of terminology in articles according to the medical specialty and the type of radiology journal were evaluated.
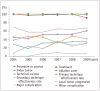
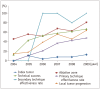
Results: Among the articles (n = 308) included in this study, the accuracy of the terms 'procedure or session', 'treatment', 'index tumor', 'ablation zone', 'technical success', 'primary technique effectiveness rate', 'secondary technique effectiveness rate', 'local tumor progression', 'major complication', and 'minor complication' was 97% (298/307), 97% (291/300), 8% (25/307), 65% (103/159), 55% (52/94), 33% (42/129), 94% (17/18), 45% (88/195), 99% (79/80), and 100% (77/77), respectively. The overall accuracy of each term showed a tendency to improve over the years. The most commonly used alternative terms for 'technical success' and 'local tumor progression' were 'complete ablation' and 'local (tumor) recurrence', respectively. The accuracy of terminology in articles published in radiology journals was significantly greater than that of terminology in articles published in non-radiology journals, especially in Radiology and The Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology.
Conclusion: The proposal for standardization of terminology and reporting criteria for RF tumor ablation has been gaining support according to the recently published scientific reports, especially in the field of radiology. However, more work is still needed for the complete standardization of terminology.
Keywords: Ablation techniques; Neoplasms; Reference standards; Review; Terminology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria.J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2005 Jun;16(6):765-78. doi: 10.1097/01.RVI.0000170858.46668.65. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2005. PMID: 15947040
-
Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria--a 10-year update.J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014 Nov;25(11):1691-705.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2014.08.027. Epub 2014 Oct 23. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014. PMID: 25442132 Free PMC article.
-
Endovascular radiofrequency ablation for varicose veins: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2011;11(1):1-93. Epub 2011 Feb 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2011. PMID: 23074413 Free PMC article.
-
Image-Guided Thyroid Ablation: Proposal for Standardization of Terminology and Reporting Criteria.Thyroid. 2019 May;29(5):611-618. doi: 10.1089/thy.2018.0604. Epub 2019 Apr 12. Thyroid. 2019. PMID: 30803397
-
Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria--a 10-year update: supplement to the consensus document.J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014 Nov;25(11):1706-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2014.09.005. Epub 2014 Oct 23. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014. PMID: 25442133 No abstract available.
Cited by
-
US-Guided Percutaneous Radiofrequency versus Microwave Ablation for Benign Thyroid Nodules: A Prospective Multicenter Study.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 25;7(1):9554. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09930-7. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28842651 Free PMC article.
-
The Islanding effect - a special method of percutaneous peritumor ethanol injection for hepatocellular carcinoma: 15-year follow-up outcome.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Jan 22;100(3):e24365. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000024365. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33546073 Free PMC article.
-
Urgent need to apply a common language in image-guided thermal ablations.J Ultrasound. 2018 Mar;21(1):77-78. doi: 10.1007/s40477-017-0278-x. Epub 2018 Jan 8. J Ultrasound. 2018. PMID: 29374402 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Microwave Ablation Compared With Laser Ablation for Treating Benign Thyroid Nodules in a Propensity-Score Matching Study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 Dec 13;10:874. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00874. eCollection 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 31920983 Free PMC article.
-
Quality Reporting of Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis According to PRISMA 2020 Guidelines: Results from Recently Published Papers in the Korean Journal of Radiology.Korean J Radiol. 2022 Mar;23(3):355-369. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2021.0808. Korean J Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35213097 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Winter TC, Laeseke PF, Lee FT., Jr Focal tumor ablation: a new era in cancer therapy. Ultrasound Q. 2006;22:195–217. - PubMed
-
- Smith KA, Kim HS. Interventional radiology and image-guided medicine: interventional oncology. Semin Oncol. 2011;38:151–162. - PubMed
-
- Kurup AN, Callstrom MR. Ablation of skeletal metastases: current status. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2010;21(8 Suppl):S242–S250. - PubMed
-
- Pua BB, Thornton RH, Solomon SB. Ablation of pulmonary malignancy: current status. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2010;21(8 Suppl):S223–S232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

