Toll-like receptor 4 limits transmission of Bordetella bronchiseptica
- PMID: 24497924
- PMCID: PMC3907416
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085229
Toll-like receptor 4 limits transmission of Bordetella bronchiseptica
Abstract
Transmission of pathogens has been notoriously difficult to study under laboratory conditions leaving knowledge gaps regarding how bacterial factors and host immune components affect the spread of infections between hosts. We describe the development of a mouse model of transmission of a natural pathogen, Bordetella bronchiseptica, and its use to assess the impact of host immune functions. Although B. bronchiseptica transmits poorly between wild-type mice and mice lacking other immune components, it transmits efficiently between mice deficient in Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4). TLR4-mutant mice were more susceptible to initial colonization, and poorly controlled pathogen growth and shedding. Heavy neutrophil infiltration distinguished TLR4-deficient responses, and neutrophil depletion did not affect respiratory CFU load, but decreased bacterial shedding. The effect of TLR4 response on transmission may explain the extensive variation in TLR4 agonist potency observed among closely related subspecies of Bordetella. This transmission model will enable mechanistic studies of how pathogens spread from one host to another, the defining feature of infectious disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
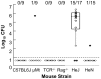
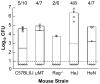


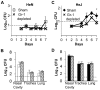
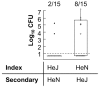
Similar articles
-
Enzymatic modification of lipid A by ArnT protects Bordetella bronchiseptica against cationic peptides and is required for transmission.Infect Immun. 2014 Feb;82(2):491-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01260-12. Epub 2013 Oct 14. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 24478065 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative toll-like receptor 4-mediated innate host defense to Bordetella infection.Infect Immun. 2005 Dec;73(12):8144-52. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.12.8144-8152.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 16299309 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor 4-dependent early elicited tumor necrosis factor alpha expression is critical for innate host defense against Bordetella bronchiseptica.Infect Immun. 2004 Nov;72(11):6650-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.11.6650-6658.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15501798 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental sensing mechanisms in Bordetella.Adv Microb Physiol. 2001;44:141-81. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(01)44013-6. Adv Microb Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11407112 Review.
-
Bordetella bronchiseptica infection of rats and mice.Comp Med. 2003 Feb;53(1):11-20. Comp Med. 2003. PMID: 12625502 Review.
Cited by
-
Enzymatic modification of lipid A by ArnT protects Bordetella bronchiseptica against cationic peptides and is required for transmission.Infect Immun. 2014 Feb;82(2):491-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01260-12. Epub 2013 Oct 14. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 24478065 Free PMC article.
-
An Extracellular Polysaccharide Locus Required for Transmission of Bordetella bronchiseptica.J Infect Dis. 2017 Oct 17;216(7):899-906. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix251. J Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28973366 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Bacterial Colonization of the Respiratory Tract.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2015;69:425-44. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-091014-104209. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26488280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bordetella pertussis transmission.Pathog Dis. 2015 Nov;73(8):ftv068. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftv068. Epub 2015 Sep 14. Pathog Dis. 2015. PMID: 26374235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gastrointestinal helminths increase Bordetella bronchiseptica shedding and host variation in supershedding.Elife. 2022 Nov 8;11:e70347. doi: 10.7554/eLife.70347. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36346138 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brockmeier SL, Lager KM (2002) Experimental airborne transmission of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus and Bordetella bronchiseptica. Vet Microbiol 89: 267–275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

