Identification of STAT5A and STAT5B target genes in human T cells
- PMID: 24497979
- PMCID: PMC3907443
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086790
Identification of STAT5A and STAT5B target genes in human T cells
Abstract
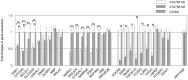
Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) comprises a family of universal transcription factors that help cells sense and respond to environmental signals. STAT5 refers to two highly related proteins, STAT5A and STAT5B, with critical function: their complete deficiency is lethal in mice; in humans, STAT5B deficiency alone leads to endocrine and immunological problems, while STAT5A deficiency has not been reported. STAT5A and STAT5B show peptide sequence similarities greater than 90%, but subtle structural differences suggest possible non-redundant roles in gene regulation. However, these roles remain unclear in humans. We applied chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by DNA sequencing using human CD4(+) T cells to detect candidate genes regulated by STAT5A and/or STAT5B, and quantitative-PCR in STAT5A or STAT5B knock-down (KD) human CD4(+) T cells to validate the findings. Our data show STAT5A and STAT5B play redundant roles in cell proliferation and apoptosis via SGK1 interaction. Interestingly, we found a novel, unique role for STAT5A in binding to genes involved in neural development and function (NDRG1, DNAJC6, and SSH2), while STAT5B appears to play a distinct role in T cell development and function via DOCK8, SNX9, FOXP3 and IL2RA binding. Our results also suggest that one or more co-activators for STAT5A and/or STAT5B may play important roles in establishing different binding abilities and gene regulation behaviors. The new identification of these genes regulated by STAT5A and/or STAT5B has major implications for understanding the pathophysiology of cancer progression, neural disorders, and immune abnormalities.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Lin JX, Leonard WJ (2000) The role of Stat5a and Stat5b in signaling by IL-2 family cytokines. Oncogene 19: 2566–2576. - PubMed
-
- Leonard WJ, O'Shea JJ (1998) Jaks and STATs: biological implications. Annu Rev Immunol 16: 293–322. - PubMed
-
- Lin JX, Mietz J, Modi WS, John S, Leonard WJ (1996) Cloning of human Stat5B. Reconstitution of interleukin-2-induced Stat5A and Stat5B DNA binding activity in COS-7 cells. J Biol Chem 271: 10738–10744. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

