Single and combined effects of deoxynivalenol mycotoxin and a microbial feed additive on lymphocyte DNA damage and oxidative stress in broiler chickens
- PMID: 24498242
- PMCID: PMC3909330
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088028
Single and combined effects of deoxynivalenol mycotoxin and a microbial feed additive on lymphocyte DNA damage and oxidative stress in broiler chickens
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e100907
Abstract
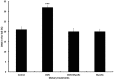
The immune and intestinal epithelial cells are particularly sensitive to the toxic effects of deoxynivalenol (DON). The aim of this experiment was to study the effects of DON and/or a microbial feed additive on the DNA damage of blood lymphocytes and on the level of thiobarbituric acid reactive substance (TBARS) as an indicator of lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress in broilers. A total of forty 1-d-old broiler chicks were randomly assigned to 1 of 4 dietary treatments (10 birds per group) for 5 wk. The dietary treatments were 1) basal diet; 2) basal diet contaminated with 10 mg DON/kg feed; 3) basal diet contaminated with 10 mg DON/kg feed and supplemented with 2.5 kg/ton of feed of Mycofix Select; 4) basal diet supplemented with Mycofix Select (2.5 kg/ton of feed). At the end of the feeding trial, blood were collected for measuring the level of lymphocyte DNA damage of blood and the TBARS level was measured in plasma, heart, kidney, duodenum and jejunum. The dietary exposure of DON caused a significant increase (P = 0.001) of DNA damage in blood lymphocytes (31.99 ± 0.89%) as indicated in the tail of comet assay. Interestingly addition of Mycofix Select to DON contaminated diet decreased (P = 0.001) the DNA damage (19.82 ± 1.75%) induced by DON. In order to clarify the involvement of lipid peroxidation in the DNA damage of DON, TBARS levels was measured. A significant increase (P = 0.001) in the level of TBARS (23 ± 2 nmol/mg) was observed in the jejunal tissue suggesting that the lipid peroxidation might be involved in the DNA damage. The results indicate that DON is cytotoxic and genotoxic to the chicken intestinal and immune cells and the feed additive have potential ability to prevent DNA damage induced by DON.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Pestka JJ, Zhou HR, Moon Y, Chung YJ (2004) Cellular and molecular mechanisms for immune modulation by deoxynivalenol and other trichothecenes: Unraveling a paradox. Toxicol Lett 153: 61–73. - PubMed
-
- Dvorska JE, Pappas AC, Karadas F, Speake BK, Surai PF (2007) Protective effect of modified glucomannans and organic selenium against antioxidant depletion in the chicken liver due to T-2 toxin-contaminated feed consumption. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 145: 582–587. - PubMed
-
- Rizzo AF, Atroshi F, Ahotupa M, Sankari S, Elovaara E (1994) Protective effect of antioxidants against free radical-mediated lipid peroxidation induced by DON or T-2 toxin. Zentralbl Veterinarmed A 41: 81–90. - PubMed
-
- Atroshi F, Rizzo A, Biese I, Veijalainen P, Antila E, et al. (1997) T-2 toxin-induced DNA damage in mouse livers: the effect of pretreatment with coenzyme Q10 and alpha-tocopherol. Mol Aspects Med 18: S255–S258. - PubMed
-
- Leal M, Shimada A, Ruiz F, Gonzalez de ME (1999) Effect of lycopene on lipid peroxidation and glutathione-dependent enzymes induced by T-2 toxin in vivo. Toxicol Lett 109: 1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

