Host specificity and co-speciation in avian haemosporidia in the Western Cape, South Africa
- PMID: 24498273
- PMCID: PMC3911919
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086382
Host specificity and co-speciation in avian haemosporidia in the Western Cape, South Africa
Erratum in
-
Correction: Host specificity and co-speciation in avian haemosporidia in the Western Cape, South Africa.PLoS One. 2015 May 20;10(5):e0129188. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129188. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25992794 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
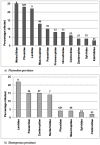
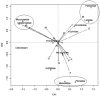
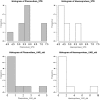
Host and pathogen ecology are often closely linked, with evolutionary processes often leading to the development of host specificity traits in some pathogens. Host specificity may range from 'generalist', where pathogens infect any available competent host; to 'specialist', where pathogens repeatedly infect specific host species or families. Avian malaria ecology in the region remains largely unexplored, despite the presence of vulnerable endemic avian species. We analysed the expression of host specificity in avian haemosporidia, by applying a previously developed host specificity index to lineages isolated from wetland passerines in the Western Cape, South Africa. Parasite lineages were isolated using PCR and identified when possible using matching lineages deposited in GenBank and in MalAvi. Parasitic clades were constructed from phylogenetic trees consisting of Plasmodium and Haemoproteus lineages. Isolated lineages matched some strains of Plasmodium relictum, P. elongatum, Haemoproteus sylvae and H. lanii. Plasmodium lineages infected a wide range of hosts from several avian families in a generalist pattern of infection. Plasmodium spp. also exhibited an infection trend according to host abundance rather than host species. By contrast, Haemoproteus lineages were typically restricted to one or two host species or families, and displayed higher host fidelity than Plasmodium spp. The findings confirm that a range of host specificity traits are exhibited by avian haemosporidia in the region. The traits show the potential to not only impact infection prevalence within specific host species, but also to affect patterns of infection at the community level.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Hellgren O, Waldenström J, Peréz-Tris J, Szollosi E, Si Ö, et al. (2007a) Detecting shifts of transmission areas in avian malaria parasites – a phylogenetic approach. Mol Ecol 16: 1281–1290. - PubMed
-
- Keesing F, Holt RD, Ostfeld RS (2006) Effects of species diversity on disease risk. Ecol Letters 9: 485–498. - PubMed
-
- Ostfeld RS, Keesing F (2000) Biodiversity series: the function of biodiversity in the ecology of vector-borne zoonotic diseases. Can J Zool 78: 2061–2078.
-
- Beadell JS, Gering E, Austin J, Dumbacher P, Peirce MA, et al. (2004) Prevalence and differential host-specificity of two avian blood parasite genera in the Australo-Papuan region. Mol Ecol 13: 3829–3844. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

