The candidate TB vaccine, MVA85A, induces highly durable Th1 responses
- PMID: 24498312
- PMCID: PMC3911992
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087340
The candidate TB vaccine, MVA85A, induces highly durable Th1 responses
Abstract
Background: Vaccination against tuberculosis (TB) should provide long-term protective immunity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M.tb). The current TB vaccine, Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG), protects against disseminated childhood TB, but protection against lung TB in adolescents and adults is variable and mostly poor. One potential reason for the limited durability of protection may be waning of immunity through gradual attrition of BCG-induced T cells. We determined if a MVA85A viral-vector boost could enhance the durability of mycobacteria-specific T cell responses above those induced by BCG alone.
Methods: We describe a long-term follow-up study of persons previously vaccinated with MVA85A. We performed a medical history and clinical examination, a tuberculin skin test and measured vaccine-specific T cell responses in persons previously enrolled as adults, adolescents, children or infants into three different Phase II trials, between 2005 and 2011.
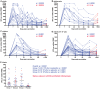
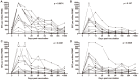
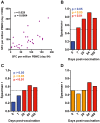
Results: Of 252 potential participants, 183 (72.6%) consented and completed the study visit. Vaccine-induced Ag85A-specific CD4+ T cell responses were remarkably persistent in healthy, HIV-uninfected adults, adolescents, children and infants, up to 6 years after MVA85A vaccination. Specific CD4+ T cells expressed surface markers consistent with either CD45RA-CCR7+ central memory or CD45RA-CCR7- effector memory T cells. Similarly durable Ag85A-specific CD4+ T cell responses were detected in HIV-infected persons who were on successful antiretroviral therapy when MVA85A was administered. By contrast, Ag85A-specific CD4+ T cell frequencies in untreated MVA85A-vaccinated HIV-infected persons were mostly undetectable 3-5 years after vaccination.
Conclusion: MVA85A induces remarkably durable T cell responses in immunocompetent persons. However, results from a recent phase IIb trial of MVA85A, conducted in infants from the same geographic area and study population, showed no vaccine efficacy, suggesting that these durable T cell responses do not enhance BCG-induced protection against TB in infants.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organisation (2013) Global Tuberculosis Report 2013.
-
- Walzl G, Ronacher K, Hanekom W, Scriba TJ, Zumla A (2011) Immunological biomarkers of tuberculosis. Nat Rev Immunol 11: 343–354. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

