Key molecular requirements for raft formation in lipid/cholesterol membranes
- PMID: 24498317
- PMCID: PMC3911970
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087369
Key molecular requirements for raft formation in lipid/cholesterol membranes
Abstract
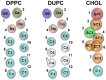
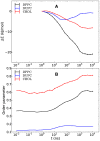
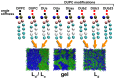
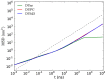
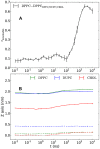
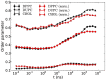
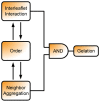
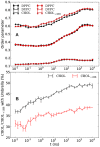
The lipid mixture of DPPC (saturated lipid)/DUPC (unsaturated lipid)/CHOL (cholesterol) is studied with respect to its ability to form liquid-ordered and liquid-disordered phases. We employ coarse-grained simulations with MARTINI force field. All three components are systematically modified in order to explore the relevant molecular properties, leading to phase separation. Specifically, we show that the DPPC/DUPC/CHOL system unmixes due to enthalpic DPPC-DPPC and DPPC-CHOL interactions. The phase separation remains unchanged, except for the formation of a gel phase at long times after decreasing the conformational degrees of freedom of the unsaturated DUPC. In contrast, the phase separation can be suppressed by softening the DPPC chains. In an attempt to mimic the ordering and unmixing effect of CHOL the latter is replaced by a stiff and shortened DPPC-like lipid. One still observes phase separation, suggesting that it is mainly the rigid and planar structure of CHOL which is important for raft formation. Addition of an extra bead to the head of CHOL has no notable impact on the phase separation of the system, supporting the irrelevance of the Umbrella model for the phase separation. Reduction of the conformational entropy of CHOL by stiffening its last bead results in a significant increase of the order of the DPPC/CHOL domain. This suggests that the conformational entropy of CHOL is important to prohibit the gelation process. The interleaflet interactions as mediated by the terminal molecular groups seem to have a strong impact on the possibility of a subsequent gelation process after phase separation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
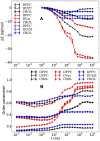
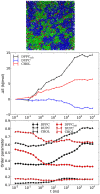
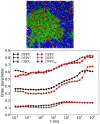
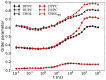
References
-
- Simons K, Ikonen E (1997) Functional rafts in cell membranes. Nature 387: 569–572. - PubMed
-
- Lingwood D, Simons K (2010) Lipid Rafts As a Membrane-Organizing Principle. Science 327: 46–50. - PubMed
-
- Simons K, Vaz WLC (2004) Model systems, lipid rafts, and cell membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 33: 269–295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

