Introduction of mismatches in a random shRNA-encoding library improves potency for phenotypic selection
- PMID: 24498319
- PMCID: PMC3911983
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087390
Introduction of mismatches in a random shRNA-encoding library improves potency for phenotypic selection
Abstract
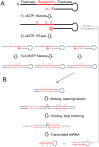
RNA interference (RNAi) is a mechanism for interfering with gene expression through the action of small, non-coding RNAs. We previously constructed a short-hairpin-loop RNA (shRNA) encoding library that is random at the nucleotide level [1]. In this library, the stems of the hairpin are completely complementary. To improve the potency of initial hits, and therefore signal-to-noise ratios in library screening, as well as to simplify hit-sequence retrieval by PCR, we constructed a second-generation library in which we introduced random mismatches between the two halves of the stem of each hairpin, on a random template background. In a screen for shRNAs that protect an interleukin-3 (IL3) dependent cell line from IL3 withdrawal, our second-generation library yielded hit sequences with significantly higher potencies than those from the first-generation library in the same screen. Our method of random mutagenesis was effective for a random template and is likely suitable, therefore, for any DNA template of interest. The improved potency of our second-generation library expands the range of possible unbiased screens for small-RNA therapeutics and biologic tools.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
A random shRNA-encoding library for phenotypic selection and hit-optimization.PLoS One. 2008 Sep 9;3(9):e3171. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003171. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18779859 Free PMC article.
-
A shRNA library constructed through the generation of loop-stem-loop DNA.J Gene Med. 2010 Nov;12(11):927-33. doi: 10.1002/jgm.1513. Epub 2010 Oct 29. J Gene Med. 2010. PMID: 21105152
-
Enzymatic production of RNAi libraries from cDNAs and high-throughput selection of effective shRNA expression constructs.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;729:123-39. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-065-2_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21365487
-
Enzymatically prepared RNAi libraries.Nat Methods. 2006 Sep;3(9):696-700. doi: 10.1038/nmeth912. Nat Methods. 2006. PMID: 16929314 Review.
-
[Application of RNAi library to oncology investigation].Ai Zheng. 2008 Nov;27(11):1229-32. Ai Zheng. 2008. PMID: 19000460 Review. Chinese.
References
-
- Hammond SM (2005) Dicing and slicing: the core machinery of the RNA interference pathway. FEBS Lett 579: 5822–5829. - PubMed
-
- Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson A, Schelter JM, et al. (2005) Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large numbers of target mRNAs. Nature 433: 769–773. - PubMed
-
- Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120: 15–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

