Myeloid deletion of SIRT1 aggravates serum transfer arthritis in mice via nuclear factor-κB activation
- PMID: 24498364
- PMCID: PMC3912001
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087733
Myeloid deletion of SIRT1 aggravates serum transfer arthritis in mice via nuclear factor-κB activation
Abstract
Objective: SIRT1 modulates the acetylation of the p65 subunit of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and plays a pivotal role in the inflammatory response. This study sought to assess the role of SIRT1 in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) using a myeloid cell-specific SIRT1 knockout (mSIRT1 KO) mouse.
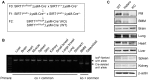
Methods: mSIRT1 KO mice were generated using the loxP/Cre recombinase system. K/BxN serum transfer arthritis was induced in mSIRT1 KO mice and age-matched littermate loxP control mice. Arthritis severity was assessed by clinical and pathological scoring. The levels of inflammatory cytokines in the serum and joints were measured by ELISA. Migration, M1 polarization, cytokine production, osteoclastogenesis, and p65 acetylation were assessed in bone marrow-derived monocytes/macrophages (BMMs).
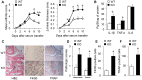
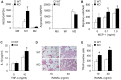
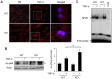
Results: mSIRT1 KO mice showed more severe inflammatory arthritis and aggravated pathological findings than control mice. These effects were paralleled by increases in IL-1, TNF-α, TRAP-positive osteoclasts, and F4/80⁺ macrophages in the ankles of mSIRT1 KO mice. In addition, BMMs from mSIRT1 KO mice displayed hyperacetylated p65 and increased NF-κB binding activity when compared to control mice, which resulted in increased M1 polarization, migration, pro-inflammatory cytokine production, and osteoclastogenesis.
Conclusion: Our study provides in vivo evidence that myeloid cell-specific deletion of SIRT1 exacerbates inflammatory arthritis via the hyperactivation of NF-κB signaling, which suggests that SIRT1 activation may be beneficial in the treatment of inflammatory arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Myeloid deletion of SIRT1 suppresses collagen-induced arthritis in mice by modulating dendritic cell maturation.Exp Mol Med. 2016 Mar 18;48(3):e221. doi: 10.1038/emm.2015.124. Exp Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 26987484 Free PMC article.
-
Myeloid deletion of SIRT1 induces inflammatory signaling in response to environmental stress.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Oct;30(19):4712-21. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00657-10. Epub 2010 Jul 20. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20647536 Free PMC article.
-
Polyphyllin I Ameliorates Collagen-Induced Arthritis by Suppressing the Inflammation Response in Macrophages Through the NF-κB Pathway.Front Immunol. 2018 Sep 27;9:2091. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02091. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30319603 Free PMC article.
-
[The cytokine homeostasis was regulated by over-expression of Sirt1 in collagen-induced arthritis mice].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2014 Oct;30(10):1034-8. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25270204 Chinese.
-
Myricetin inhibits TNF-α-induced inflammation in A549 cells via the SIRT1/NF-κB pathway.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2020 Dec;65:102000. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2021.102000. Epub 2021 Feb 16. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2020. PMID: 33601000 Review.
Cited by
-
Iguratimod promotes transformation of mononuclear macrophages in elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis by nuclear factor-κB pathway.World J Clin Cases. 2021 Apr 6;9(10):2181-2191. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i10.2181. World J Clin Cases. 2021. PMID: 33869594 Free PMC article.
-
Sirtuin 2 Deficiency Increases Bacterial Phagocytosis by Macrophages and Protects from Chronic Staphylococcal Infection.Front Immunol. 2017 Aug 28;8:1037. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01037. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28894448 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased SIRT1 expression in the peripheral blood of patients with Graves' disease.J Endocrinol. 2020 Aug;246(2):161-173. doi: 10.1530/JOE-19-0501. J Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32485674 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT1/Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase α Signaling Enhances Macrophage Polarization to an Anti-inflammatory Phenotype in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2017 Sep 15;8:1135. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01135. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28966618 Free PMC article.
-
AMPK/SIRT1 Deficiency Drives Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis in Rats by Promoting Glycolysis-Mediated Monocytes Inflammatory Polarization.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Aug 15;15:4663-4675. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S378090. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 35996683 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xie J, Zhang X, Zhang L (2013) Negative regulation of inflammation by SIRT1. Pharmacol Res 67: 60–67. - PubMed
-
- Niederer F, Ospelt C, Brentano F, Hottiger MO, Gay RE, et al. (2011) SIRT1 overexpression in the rheumatoid arthritis synovium contributes to proinflammatory cytokine production and apoptosis resistance. Ann Rheum Dis 70: 1866–1873. - PubMed
-
- Engler A, Gay RE, Michel BA, Gay S, Ospelt C (2012) SIRT6 Regulates Cigarette Smoke Induced MMP1 Expression in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblasts. ACR 2012 Abstract #437, S189–S190.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

