Long-term effect of a school-based physical activity program (KISS) on fitness and adiposity in children: a cluster-randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 24498404
- PMCID: PMC3912178
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087929
Long-term effect of a school-based physical activity program (KISS) on fitness and adiposity in children: a cluster-randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: School-based intervention studies promoting a healthy lifestyle have shown favorable immediate health effects. However, there is a striking paucity on long-term follow-ups. The aim of this study was therefore to assess the 3 yr-follow-up of a cluster-randomized controlled school-based physical activity program over nine month with beneficial immediate effects on body fat, aerobic fitness and physical activity.
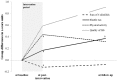
Methods and findings: Initially, 28 classes from 15 elementary schools in Switzerland were grouped into an intervention (16 classes from 9 schools, n = 297 children) and a control arm (12 classes from 6 schools, n = 205 children) after stratification for grade (1st and 5th graders). Three years after the end of the multi-component physical activity program of nine months including daily physical education (i.e. two additional lessons per week on top of three regular lessons), short physical activity breaks during academic lessons, and daily physical activity homework, 289 (58%) participated in the follow-up. Primary outcome measures included body fat (sum of four skinfolds), aerobic fitness (shuttle run test), physical activity (accelerometry), and quality of life (questionnaires). After adjustment for grade, gender, baseline value and clustering within classes, children in the intervention arm compared with controls had a significantly higher average level of aerobic fitness at follow-up (0.373 z-score units [95%-CI: 0.157 to 0.59, p = 0.001] corresponding to a shift from the 50th to the 65th percentile between baseline and follow-up), while the immediate beneficial effects on the other primary outcomes were not sustained.
Conclusions: Apart from aerobic fitness, beneficial effects seen after one year were not maintained when the intervention was stopped. A continuous intervention seems necessary to maintain overall beneficial health effects as reached at the end of the intervention.
Trial registration: ControlledTrials.com ISRCTN15360785.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Beaglehole R, Bonita R, Horton R, Adams C, Alleyne G, et al. (2011) Priority actions for the non-communicable disease crisis. Lancet 377: 1438. - PubMed
-
- Andersen LB, Riddoch C, Kriemler S, Hills A (2011) Physical activity and cardiovascular risk factors in children. Br J Sports Med 45: 871–876. - PubMed
-
- Andersen LB, Harro M, Sardinha LB, Froberg K, Ekelund U, et al. (2006) Physical activity and clustered cardiovascular risk in children: a cross-sectional study (The European Youth Heart Study). Lancet 368: 299–304. - PubMed
-
- Brage S, Wedderkopp N, Ekelund U, Franks PW, Wareham NJ, et al. (2004) Features of the metabolic syndrome are associated with objectively measured physical activity and fitness in Danish children: the European Youth Heart Study (EYHS). Diabetes Care 27: 2141–2148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

