Characteristics of hemolytic activity induced by skin secretions of the frog Kaloula pulchra hainana
- PMID: 24499077
- PMCID: PMC3710140
- DOI: 10.1186/1678-9199-19-9
Characteristics of hemolytic activity induced by skin secretions of the frog Kaloula pulchra hainana
Abstract
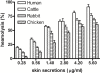
Background: The hemolytic activity of skin secretions obtained by stimulating the frog Kaloula pulchra hainana with diethyl ether was tested using human, cattle, rabbit, and chicken erythrocytes. The skin secretions had a significant concentration-dependent hemolytic effect on erythrocytes. The hemolytic activity of the skin secretions was studied in the presence of osmotic protectants (polyethylene glycols and carbohydrates), cations (Mg2+, Ca2+, Ba2+, Cu2+, and K+), or antioxidants (ascorbic acid, reduced glutathione, and cysteine).
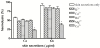
Results: Depending on their molecular mass, osmotic protectants effectively inhibited hemolysis. The inhibition of skin hemolysis was observed after treatment with polyethylene glycols (1000, 3400, and 6000 Da). Among divalent cations, only 1 mM Cu2+ markedly inhibited hemolytic activity. Antioxidant compounds slightly reduced the hemolytic activity.
Conclusions: The results suggested that skin secretions of K. pulchra hainana induce a pore-forming mechanism to form pores with a diameter of 1.36-2.0 nm rather than causing oxidative damage to the erythrocyte membrane.
Figures
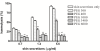
References
-
- Duellman WE, Trueb L, editor. Biology of Amphibians. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1986. pp. 197–228.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

