Asthma: Gln27Glu and Arg16Gly polymorphisms of the beta2-adrenergic receptor gene as risk factors
- PMID: 24499171
- PMCID: PMC3930554
- DOI: 10.1186/1710-1492-10-8
Asthma: Gln27Glu and Arg16Gly polymorphisms of the beta2-adrenergic receptor gene as risk factors
Abstract
Background: Asthma is caused by both environmental and genetic factors. The ADRB2 gene, which encodes the beta 2-adrenergic receptor, is one of the most extensively studied genes with respect to asthma prevalence and severity. The Arg16Gly (+46A > G) and Gln27Glu (+79C > G) polymorphisms in the ADRB2 gene cause changes in the amino acids flanking the receptor ligand site, altering the response to bronchodilators and the risk of asthma through complex pathways. The ADRB2 polymorphisms affect beta-adrenergic bronchodilator action and are a tool to identify at-risk populations.
Objective: To determine the frequency of these two polymorphisms in allergic asthma patients and healthy subjects and to correlate these data with the occurrence and severity of asthma.
Methods: Eighty-eight allergic asthma patients and 141 healthy subjects were included in this study. The ADRB2 polymorphisms were analyzed using the amplification-refractory mutation system - polymerase chain reaction (ARMS-PCR) technique. The statistical analysis was performed with the SPSS 21.0 software using the Fisher's Exact and χ2 tests.
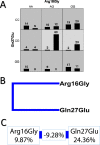
Results: The ADRB2 polymorphisms were associated with asthma occurrence. The Arg16Arg, Gln27Gln and Gln27Glu genotypes were risk factors; the odds ratios were 6.782 (CI = 3.07 to 16.03), 2.120 (CI = 1.22 to 3.71) and 8.096 (CI = 3.90 to 17.77), respectively. For the Gly16Gly and Glu27Glu genotypes, the odds ratios were 0.312 (CI = 0.17 to 0.56) and 0.084 (CI = 0.04 to 0.17), respectively. The haplotype analysis showed that there were associations between the following groups: Arg16Arg-Gln27Gln (OR = 5.108, CI = 1.82 to 16.37), Gly16Gly-Glu27Glu (OR = 2.816, CI = 1.25 to 6.54), Arg16Gly-Gln27Glu (OR = 0.048, CI = 0.01 to 0.14) and Gly16Gly-Gln27Glu (OR = 0.1036, CI = 0.02 to 0.39). The polymorphism Gln27Glu was associated with asthma severity, as the Gln27Gln genotype was a risk factor for severe asthma (OR = 2.798, CI = 1.099 to 6.674) and the Gln27Glu genotype was a protective factor for mild (OR = 3.063, CI = 1.037 to 9.041) and severe (OR = 0.182, CI = 0.048 to 0.691) asthma.
Conclusions: The Arg16Gly and Gln27Glu polymorphisms in the ADRB2 gene are associated with asthma presence and severity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of ADRB2 polymorphisms on the efficacy of salmeterol and tiotropium in preventing COPD exacerbations: a prespecified substudy of the POET-COPD trial.Lancet Respir Med. 2014 Jan;2(1):44-53. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(13)70248-0. Epub 2013 Dec 5. Lancet Respir Med. 2014. PMID: 24461901 Clinical Trial.
-
An investigation of the association between ADRB2 gene polymorphisms and asthma in Kazakh population.Clin Respir J. 2020 Jun;14(6):514-520. doi: 10.1111/crj.13160. Epub 2020 Feb 27. Clin Respir J. 2020. PMID: 32034992
-
β2-adrenergic receptor haplotype linked to intubation and mechanical ventilation in children with asthma.J Asthma. 2012 Aug;49(6):563-8. doi: 10.3109/02770903.2012.701362. J Asthma. 2012. PMID: 22793522
-
A meta-analysis of the influence of ADRB2 genetic polymorphisms on albuterol (salbutamol) therapy in patients with asthma.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2021 Apr;87(4):1708-1716. doi: 10.1111/bcp.14570. Epub 2020 Oct 25. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32986886
-
What the Genetic Background of Individuals with Asthma and Obesity Can Reveal: Is β2-Adrenergic Receptor Gene Polymorphism Important?Pediatr Allergy Immunol Pulmonol. 2014 Sep 1;27(3):104-110. doi: 10.1089/ped.2014.0360. Pediatr Allergy Immunol Pulmonol. 2014. PMID: 25276484 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Beta 2 Adrenergic Receptor Genetic Polymorphisms in Bronchial Asthma: Relationship to Disease Risk, Severity, and Treatment Response.Lung. 2018 Dec;196(6):673-680. doi: 10.1007/s00408-018-0153-3. Epub 2018 Sep 3. Lung. 2018. PMID: 30178312
-
Leveraging electronic health records to assess the role of ADRB2 single nucleotide polymorphisms in predicting exacerbation frequency in asthma patients.Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2018 Nov;28(11):256-259. doi: 10.1097/FPC.0000000000000355. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30334910 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Modifying Factors of Cystic Fibrosis Phenotype: A Challenge for Modern Medicine.J Clin Med. 2021 Dec 13;10(24):5821. doi: 10.3390/jcm10245821. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34945117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repeated-Dose Toxicity of Lauric Acid and Its Preventive Effect Against Tracheal Hyper-Responsiveness in Wistar Rats with Possible In Silico Molecular Targets.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Feb 6;18(2):221. doi: 10.3390/ph18020221. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40006035 Free PMC article.
-
Association of β2-adrenergic receptor gene polymorphisms (rs1042713, rs1042714, rs1042711) with asthma risk: a systematic review and updated meta-analysis.BMC Pulm Med. 2019 Nov 7;19(1):202. doi: 10.1186/s12890-019-0962-z. BMC Pulm Med. 2019. PMID: 31699066 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) A pocket guide for asthma management and prevention (for adults and children older than 5 years) 2012. Available from: http://www.ginasthma.com.
-
- Worldwide variation in prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivities, and atopic eczema. ISACC: The International Study of asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC) - Steering Committee. Lancet. 1998;351(111):125–132. - PubMed
-
- Brasil. Ministério da Saúde. Secretaria nacional de Ações Básicas. Estatísticas de Saúde e Mortalidade. Brasília: Ministério da Saúde; 2005.
-
- Hogg A. Asthma in children. InnovAiT. 2011;4(3):160–170.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

