Biological degradation of catechol in wastewater using the sequencing continuous-inflow reactor (SCR)
- PMID: 24499534
- PMCID: PMC3776296
- DOI: 10.1186/2052-336X-11-3
Biological degradation of catechol in wastewater using the sequencing continuous-inflow reactor (SCR)
Abstract
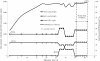
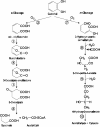
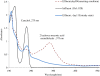
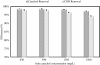
Catechol is used in many industries. It can be removed from wastewater by various methods but biological processes are the most superior and commonly used technology. The SCR is a modified form of SBR used to degrade catechol. The objective of this study was to investigate the performance of SCR for biodegradation and mineralization of catechol under various inlet concentrations (630-1500 mg/L) and hydraulic retention times (HRT) (18-9 h). This study used a bench scale SCR setup to test catechol degradation. The acclimation time of biomass for catechol at degradation at 630 mg/L was 41 d. The SCR operating cycle time was 6 h and the consecutive times taken for aerating, settling and decanting were 4, 1.5 and 0.5 h, respectively. This study investigated the effects of inlet catechol concentration (630-1560 mg/L) and HRT (18-9 h). The average catechol removal efficiencies in steady-state conditions of 630, 930, 12954 and 1559 mg/L of catechol were 98.5%, 98.5%, 98.2% and 96.9% in terms catechol and 97.8%, 97.7%, 96.4% and 94.3% for COD, respectively. SCR with acclimated biomasses could effectively remove the catechol and the corresponding COD from wastewater with concentrations of up to 1560, at the loading rate of 5.38 kg COD/m3.d and at a HRT of up to 13 h. The HRT was determined as an important variable affecting catechol removal from wastewater. Reducing the HRT to below 13 h led to reduced removal of catechol and COD.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Investigating the performance of a novel cyclic rotating-bed biological reactor compared with a sequencing continuous-inflow reactor for biodegradation of catechol in wastewater.Bioresour Technol. 2013 Jun;138:369-72. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2013.03.133. Epub 2013 Mar 28. Bioresour Technol. 2013. PMID: 23623431
-
Degradation and COD removal of catechol in wastewater using the catalytic ozonation process combined with the cyclic rotating-bed biological reactor.J Environ Manage. 2015 Jul 1;157:262-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.02.036. Epub 2015 Apr 24. J Environ Manage. 2015. PMID: 25913467
-
Upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor--a review.Indian J Environ Health. 2001 Apr;43(2):1-82. Indian J Environ Health. 2001. PMID: 12397675 Review.
-
Investigation of furfural biodegradation in a continuous inflow cyclic biological reactor.Water Sci Technol. 2016;73(2):292-301. doi: 10.2166/wst.2015.488. Water Sci Technol. 2016. PMID: 26819384
-
Biological removal of phenol from strong wastewaters using a novel MSBR.Water Res. 2009 Mar;43(5):1295-302. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2008.12.026. Epub 2008 Dec 25. Water Res. 2009. PMID: 19131088
Cited by
-
Multi-omics Approaches To Decipher the Impact of Diet and Host Physiology on the Mammalian Gut Microbiome.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020 Nov 10;86(23):e01864-20. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01864-20. Print 2020 Nov 10. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32948523 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Prospects of Carbonaceous Nanomaterials-Based Laccase Biosensor for Electrochemical Detection of Phenolic Compounds.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Feb 22;13(3):305. doi: 10.3390/bios13030305. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36979517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating the biological degradation of the drug β-blocker atenolol from wastewater using the SBR.Biodegradation. 2022 Jun;33(3):267-281. doi: 10.1007/s10532-022-09979-w. Epub 2022 Apr 28. Biodegradation. 2022. PMID: 35482263
-
Comparison of the rhizospheric soil bacteriomes of Oryza sativa and Solanum melongena crop cultivars reveals key genes and pathways involved in biosynthesis of ectoine, lysine, and catechol meta-cleavage.Funct Integr Genomics. 2025 Jan 21;25(1):20. doi: 10.1007/s10142-025-01536-x. Funct Integr Genomics. 2025. PMID: 39836258
-
MnO2/TiO2-Catalyzed ozonolysis: enhancing Pentachlorophenol degradation and understanding intermediates.BMC Chem. 2024 May 9;18(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s13065-024-01194-3. BMC Chem. 2024. PMID: 38725018 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lofrano G, Rizzo L, Grassi M, Belgiorno V. Advanced oxidation of catechol: A comparison among photocatalysis, Fenton and photo-Fenton processes. Desalination. 2009;249:878–883. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2009.02.068. - DOI
-
- Moussavi G, Barikbin B, Mahmoudi M. The removal of high concentrations of phenol from saline wastewater using aerobic granular SBR. Chem Eng J. 2010;158:498–504. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2010.01.038. - DOI
-
- Kumar A, Kumar S, Kumar S. Biodegradation kinetics of phenol and catechol using Pseudomonas putida MTCC 1194. Biochem Eng J. 2005;22:151–159. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2004.09.006. - DOI
-
- Rigo M, Alegre RM, Bezerra JRMV, Coelho N, Bastos RG. Catechol Biodegradation kinetics Using Candida parapsilopsis. Braz Archives Biology Technology. 2010;53:481–486. doi: 10.1590/S1516-89132010000200029. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

