Epstein-Barr Virus encoded LMP1 regulates cyclin D1 promoter activity by nuclear EGFR and STAT3 in CNE1 cells
- PMID: 24499623
- PMCID: PMC3843577
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-9966-32-90
Epstein-Barr Virus encoded LMP1 regulates cyclin D1 promoter activity by nuclear EGFR and STAT3 in CNE1 cells
Abstract
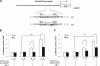
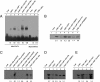
The principal Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) oncoprotein, latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) is strongly associated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), a prevalent cancer in China. The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is important in carcinogenesis, as it is a ubiquitously expressed receptor tyrosine kinase. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is a master transcriptional regulator in proliferation and apoptosis. Our previous study demonstrated that the nuclear EGFR could bind to the cyclin D1 promoter directly in the presence of LMP1, and the correlation between EGFR and STAT3 in NPC remains to be further explored. Here, we have shown that the interaction of EGFR and STAT3 increased in the nucleus in the presence of LMP1. LMP1 promoted both EGFR and STAT3 binding to the promoter region of cyclin D1, in turn, enhancing the promoter activity of cyclin D1. Furthermore, we demonstrated that both transcriptional activity and mRNA levels of cyclin D1 were decreased by small molecule interference of EGFR and STAT3 activity. These findings may provide a novel linkage between the EGFR and STAT3 signaling pathways and the activation of cyclin D1 by LMP1 in the carcinogenesis of NPC.
Figures


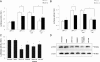
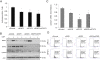
Similar articles
-
Nuclear accumulation of epidermal growth factor receptor and acceleration of G1/S stage by Epstein-Barr-encoded oncoprotein latent membrane protein 1.Exp Cell Res. 2005 Feb 15;303(2):240-51. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.09.030. Epub 2004 Nov 11. Exp Cell Res. 2005. PMID: 15652339
-
Positive regulation of HIF-1A expression by EBV oncoprotein LMP1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells.Cancer Lett. 2016 Nov 1;382(1):21-31. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.08.021. Epub 2016 Aug 24. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 27567526
-
Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 induces expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor through effects on Bcl-3 and STAT3.J Virol. 2008 Jun;82(11):5486-93. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00125-08. Epub 2008 Mar 26. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18367518 Free PMC article.
-
Novel roles and therapeutic targets of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1-induced oncogenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2015 Aug 18;17:e15. doi: 10.1017/erm.2015.13. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 26282825 Review.
-
Modulation of the tumor microenvironment by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Cancer Sci. 2018 Feb;109(2):272-278. doi: 10.1111/cas.13473. Epub 2018 Jan 21. Cancer Sci. 2018. PMID: 29247573 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of Epstein-Barr virus infection in the pathogenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Virol Sin. 2015 Apr;30(2):107-21. doi: 10.1007/s12250-015-3592-5. Epub 2015 Apr 21. Virol Sin. 2015. PMID: 25910483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Progression: Accumulating Genomic Instability and Persistent Epstein-Barr Virus Infection.Curr Oncol. 2022 Aug 23;29(9):6035-6052. doi: 10.3390/curroncol29090475. Curr Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36135044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles and Ebola Virus: A New Mechanism of Immune Evasion.Viruses. 2019 May 2;11(5):410. doi: 10.3390/v11050410. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31052499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Knockdown of LMP1-induced miR-155 sensitizes nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells to radiotherapy in vitro.Oncol Lett. 2016 May;11(5):3451-3456. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4400. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27123134 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Virus-Induced EGFR Trafficking in Proviral Functions.Biomolecules. 2023 Dec 9;13(12):1766. doi: 10.3390/biom13121766. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 38136637 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Raab-Traub N. In: DNA tumor viruses. Damania B, Pipas JM, editor. New York, NY: Springer; 2009. Epstein–Barr virus transforming proteins: biologic properties and contribution to oncogenesis; pp. 259–284.
-
- Strong MJ, Xu G, Coco J, Baribault C, Vinay DS, Lacey MR, Strong AL, Lehman TA, Seddon MB, Lin Z. et al.Differences in gastric carcinoma microenvironment stratify according to EBV infection intensity: implications for possible immune adjuvant therapy. PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(5):e1003341. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003341. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- van Beek J, zur Hausen A, Klein Kranenbarg E, van de Velde CJ, Middeldorp JM, van den Brule AJ, Meijer CJ, Bloemena E. EBV-positive gastric adenocarcinomas: a distinct clinicopathologic entity with a low frequency of lymph node involvement. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22(4):664–670. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2004.08.061. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sasagawa T, Shimakage M, Nakamura M, Sakaike J, Ishikawa H, Inoue M. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genes expression in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and invasive cervical cancer: a comparative study with human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. Hum Pathol. 2000;31(3):318–326. doi: 10.1016/S0046-8177(00)80245-2. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

