Evaluation of von Willebrand factor and von Willebrand factor propeptide in models of vascular endothelial cell activation, perturbation, and/or injury
- PMID: 24499802
- PMCID: PMC4222990
- DOI: 10.1177/0192623313518664
Evaluation of von Willebrand factor and von Willebrand factor propeptide in models of vascular endothelial cell activation, perturbation, and/or injury
Abstract
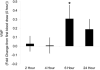
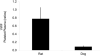
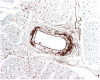
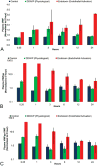
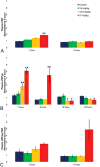
Pharmacologically, vasoactive agents targeting endothelial and/or smooth muscle cells (SMC) are known to cause acute drug-induced vascular injury (DIVI) and the resulting pathology is due to endothelial cell (EC) perturbation, activation, and/or injury. Alteration in EC structure and/or function may be a critical event in vascular injury and, therefore, evaluation of the circulatory kinetic profile and secretory pattern of EC-specific proteins such as VWF and VWFpp could serve as acute vascular injury biomarkers. In rat and dog models of DIVI, this profile was determined using pharmacologically diverse agents associated with functional stimulation/perturbation (DDAVP), pathological activation (lipopolysaccharide [LPS]/endotoxin), and structural damage (fenoldopam [FD], dopamine [DA], and potassium channel opener (PCO) ZD6169). In rats, FD caused moderate DIVI and time-related increase in plasma VWF levels ∼33% while in control rats VWF increased ∼5%. In dogs, VWF levels transiently increased ∼30% when there was morphologic evidence of DIVI by DA or ZD6169. However, in dogs, VWFpp increased >60-fold (LPS) and >6-fold (DDAVP), respectively. This was in comparison to smaller dynamic 1.38-fold (LPS) and 0.54-fold (DDAVP) increases seen in plasma VWF. Furthermore, DA was associated with a dose-dependent increase in plasma VWFpp. In summary, VWF and VWFpp can discriminate between physiological and pathological perturbation, activation, and injury to ECs.
Keywords: DDAVP.; DIVI; LPS; VWF; VWFpp; activation; biomarker; dog; endothelial cell; perturbation; rat.
© 2014 by The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

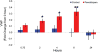

Similar articles
-
von Willebrand factor propeptide to antigen ratio identifies platelet activation and reduced von Willebrand factor survival phenotype in mice.J Thromb Haemost. 2018 Mar;16(3):546-554. doi: 10.1111/jth.13934. Epub 2018 Jan 24. J Thromb Haemost. 2018. PMID: 29285851 Free PMC article.
-
Von Willebrand factor propeptide in severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): evidence of acute and sustained endothelial cell activation.Br J Haematol. 2021 Feb;192(4):714-719. doi: 10.1111/bjh.17273. Epub 2020 Dec 16. Br J Haematol. 2021. PMID: 33326604
-
Genome-wide studies of von Willebrand factor propeptide identify loci contributing to variation in propeptide levels and von Willebrand factor clearance.J Thromb Haemost. 2016 Sep;14(9):1888-98. doi: 10.1111/jth.13401. Epub 2016 Aug 19. J Thromb Haemost. 2016. PMID: 27359253 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of von Willebrand factor propeptide improves the diagnosis of von Willebrand disease.Semin Thromb Hemost. 2011 Jul;37(5):456-63. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1281029. Epub 2011 Nov 18. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2011. PMID: 22102187 Review.
-
Laboratory diagnosis and molecular classification of von Willebrand disease.Acta Haematol. 2009;121(2-3):71-84. doi: 10.1159/000214846. Epub 2009 Jun 8. Acta Haematol. 2009. PMID: 19506352 Review.
Cited by
-
Prospective Evaluation of the Pre-, Intra-, and Postoperative Kinetics of ADAMTS-13, von Willebrand Factor, and Interleukin-6 in Vascular Surgery.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2020 Jan-Dec;26:1076029620930273. doi: 10.1177/1076029620930273. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2020. PMID: 33023308 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment with ddAVP improves platelet-based coagulation in a rat model of traumatic hemorrhagic shock.Trauma Surg Acute Care Open. 2022 Mar 8;7(1):e000852. doi: 10.1136/tsaco-2021-000852. eCollection 2022. Trauma Surg Acute Care Open. 2022. PMID: 35340703 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Nitinol on Metabolic and Coagulation Activity of Endothelial Cells Culture.Bull Exp Biol Med. 2021 Aug;171(4):480-482. doi: 10.1007/s10517-021-05255-8. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 34542754
-
Endothelial alterations in a canine model of immune thrombocytopenia.Platelets. 2019;30(1):88-97. doi: 10.1080/09537104.2017.1378807. Epub 2017 Nov 28. Platelets. 2019. PMID: 29182425 Free PMC article.
-
VWF excess and ADAMTS13 deficiency: a unifying pathomechanism linking inflammation to thrombosis in DIC, malaria, and TTP.Thromb Haemost. 2015 Apr;113(4):708-18. doi: 10.1160/TH14-09-0731. Epub 2014 Dec 11. Thromb Haemost. 2015. PMID: 25503977 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Blann AD. Plasma von Willebrand factor, thrombosis, and the endothelium: The first 30 years. Thromb Haemost. 2006;95:49–55. - PubMed
-
- Borchiellini A, Fijnvandraat K, ten Cat JW, Pajkrt D, van Deventer SJ, Pasterkamp G, Meijer-Huizinga F, Zwart-Huinink L, Voorberg J, van Mourik JA. Quantitative analysis of von Willebrand factor propeptide release in vivo: Effect of experimental endotoxemia and administration of 1-deamino-8-D-arginine vasopressin in humans. Blood. 1996;88:2951–8. - PubMed
-
- Brott D, Gould S, Jones H, Schofield J, Prior H, Valentin JP, Bjurstrom S, Kenne K, Schuppe-Koistinen I, Katein A, Foster-Brown L, Betton G, Richardson R, Evans G, Louden C. Bio-markers of drug-induced vascular injury. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2005;207:S441–S5. - PubMed
-
- Brott DA, Richardson RJ, Louden CS. Evidence for the nitric oxide pathway as a potential mode of action in fenoldopam-induced vascular injury. Toxicol Pathol. 2012;40:874–86. - PubMed
-
- Castro-Nŭnez L, Dienava-Verdoold I, Herczenik E, Mertens K, Meijer AB. Shear stress is required for the endocytic uptake of the factor VIII-von Willebrand factor complex by macrophages. J Thromb Haemost. 2012;10:1929–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

