Caveolin-1 is a risk factor for postsurgery metastasis in preclinical melanoma models
- PMID: 24500501
- PMCID: PMC3999137
- DOI: 10.1097/CMR.0000000000000046
Caveolin-1 is a risk factor for postsurgery metastasis in preclinical melanoma models
Abstract
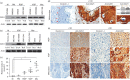
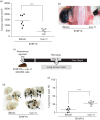
Melanomas are highly lethal skin tumours that are frequently treated by surgical resection. However, the efficacy of such procedures is often limited by tumour recurrence and metastasis. Caveolin-1 (CAV1) has been attributed roles as a tumour suppressor, although in late-stage tumours, its presence is associated with enhanced metastasis. The expression of this protein in human melanoma development and particularly how the presence of CAV1 affects metastasis after surgery has not been defined. CAV1 expression in human melanocytes and melanomas increases with disease progression and is highest in metastatic melanomas. The effect of increased CAV1 expression can then be evaluated using B16F10 murine melanoma cells injected into syngenic immunocompetent C57BL/6 mice or human A375 melanoma cells injected into immunodeficient B6Rag1-/- mice. Augmented CAV1 expression suppresses tumour formation upon a subcutaneous injection, but enhances lung metastasis of cells injected into the tail vein in both models. A procedure was initially developed using B16F10 melanoma cells in C57BL/6 mice to mimic better the situation in patients undergoing surgery. Subcutaneous tumours of a defined size were removed surgically and local tumour recurrence and lung metastasis were evaluated after another 14 days. In this postsurgery setting, CAV1 presence in B16F10 melanomas favoured metastasis to the lung, although tumour suppression at the initial site was still evident. Similar results were obtained when evaluating A375 cells in B6Rag1-/- mice. These results implicate CAV1 expression in melanomas as a marker of poor prognosis for patients undergoing surgery as CAV1 expression promotes experimental lung metastasis in two different preclinical models.
Figures




Similar articles
-
E-cadherin determines Caveolin-1 tumor suppression or metastasis enhancing function in melanoma cells.Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2013 Jul;26(4):555-70. doi: 10.1111/pcmr.12085. Epub 2013 Apr 11. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2013. PMID: 23470013 Free PMC article.
-
CAV1 inhibits metastatic potential in melanomas through suppression of the integrin/Src/FAK signaling pathway.Cancer Res. 2010 Oct 1;70(19):7489-99. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0900. Epub 2010 Aug 13. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20709760 Free PMC article.
-
Src-family kinase inhibitors block early steps of caveolin-1-enhanced lung metastasis by melanoma cells.Biochem Pharmacol. 2020 Jul;177:113941. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.113941. Epub 2020 Mar 30. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32240650
-
Extracellular matrix-specific Caveolin-1 phosphorylation on tyrosine 14 is linked to augmented melanoma metastasis but not tumorigenesis.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 28;7(26):40571-40593. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9738. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27259249 Free PMC article.
-
Biology, Therapy and Implications of Tumor Exosomes in the Progression of Melanoma.Cancers (Basel). 2016 Dec 9;8(12):110. doi: 10.3390/cancers8120110. Cancers (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27941674 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Retrospective Cohort Study of Caveolin-1 Expression as Prognostic Factor in Unresectable Locally Advanced or Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer Patients.Curr Oncol. 2021 Sep 9;28(5):3525-3536. doi: 10.3390/curroncol28050303. Curr Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34590611 Free PMC article.
-
Maraviroc/cisplatin combination inhibits gastric cancer tumoroid growth and improves mice survival.Biol Res. 2025 Jan 18;58(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s40659-024-00581-3. Biol Res. 2025. PMID: 39827154 Free PMC article.
-
Human cancer evolution in the context of a human immune system in mice.Mol Oncol. 2018 Oct;12(10):1797-1810. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12374. Epub 2018 Sep 3. Mol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30120895 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolin-1 Y14 phosphorylation suppresses tumor growth while promoting invasion.Oncotarget. 2019 Nov 19;10(62):6668-6677. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27313. eCollection 2019 Nov 19. Oncotarget. 2019. PMID: 31803361 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolin-1-Mediated Tumor Suppression Is Linked to Reduced HIF1α S-Nitrosylation and Transcriptional Activity in Hypoxia.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Aug 20;12(9):2349. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092349. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32825247 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Quest AF, Leyton L, Parraga M.Caveolins, caveolae, and lipid rafts in cellular transport, signaling, and disease.Biochem Cell Biol 2004;82:129–144 - PubMed
-
- Quest AF, Lobos-Gonzalez L, Nunez S, Sanhueza C, Fernandez JG, Aguirre A, et al. The caveolin-1 connection to cell death and survival.Curr Mol Med 2013;13:266–281 - PubMed
-
- Nakashima H, Hamamura K, Houjou T, Taguchi R, Yamamoto N, Mitsudo K, et al. Overexpression of caveolin-1 in a human melanoma cell line results in dispersion of ganglioside GD3 from lipid rafts and alteration of leading edges, leading to attenuation of malignant properties.Cancer Sci 2007;98:512–520 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

