Structural characterization of MepB from Staphylococcus aureus reveals homology to endonucleases
- PMID: 24501097
- PMCID: PMC4005711
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.2438
Structural characterization of MepB from Staphylococcus aureus reveals homology to endonucleases
Abstract
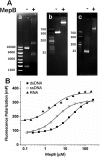
The MepRAB operon in Staphylococcus aureus has been identified to play a role in drug resistance. Although the functions of MepA and MepR are known, little information is available on the function of MepB. Here we report the X-ray structure of MepB to 2.1 Å revealing its structural similarity to the PD-(D/E)XK family of endonucleases. We further show that MepB binds DNA and RNA, with a higher affinity towards RNA and single stranded DNA than towards double stranded DNA. Notably, the PD-(D/E)XK catalytic active site residues are not conserved in MepB. MepB's association with a drug resistance operon suggests that it plays a role in responding to antimicrobials. This role is likely carried out through MepB's interactions with nucleic acids.
Keywords: DNA damage; PD-(D/E)XK endonucleases; antimicrobials; drug resistance.
© 2014 The Protein Society.
Figures
References
-
- Kaatz GW, Moudgal VV, Seo SM. Identification and characterization of a novel efflux-related multidrug resistance phenotype in Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2002;50:833–838. - PubMed
-
- Huet AA, Raygada JL, Mendiratta K, Seo SM, Kaatz GW. Multidrug efflux pump overexpression in Staphylococcus aureus after single and multiple in vitro exposures to biocides and dyes. Microbiology. 2008;154:3144–3153. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

