Genome sequence of Frateuria aurantia type strain (Kondô 67(T)), a xanthomonade isolated from Lilium auratium Lindl
- PMID: 24501647
- PMCID: PMC3910546
- DOI: 10.4056/sigs.4338002
Genome sequence of Frateuria aurantia type strain (Kondô 67(T)), a xanthomonade isolated from Lilium auratium Lindl
Abstract
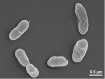
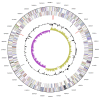
Frateuria aurantia (ex Kondô and Ameyama 1958) Swings et al. 1980 is a member of the bispecific genus Frateuria in the family Xanthomonadaceae, which is already heavily targeted for non-type strain genome sequencing. Strain Kondô 67(T) was initially (1958) identified as a member of 'Acetobacter aurantius', a name that was not considered for the approved list. Kondô 67(T) was therefore later designated as the type strain of the newly proposed acetogenic species Frateuria aurantia . The strain is of interest because of its triterpenoids (hopane family). F. aurantia Kondô 67(T) is the first member of the genus Frateura whose genome sequence has been deciphered, and here we describe the features of this organism, together with the complete genome sequence and annotation. The 3,603,458-bp long chromosome with its 3,200 protein-coding and 88 RNA genes is a part of the G enomic E ncyclopedia of Bacteria and Archaea project.
Keywords: GEBA; Xanthomonadaceae; acetogenic; mesophilic; motile; rod-shaped; strictly aerobic; ‘Acetobacter aurantius’.
Figures

References
-
- Swings J, Gillis M, Kersters K, De Vos P, Gosselé F, de Ley J. Frateuria, a new genus for " Acetobacter aurantius". Int J Syst Bacteriol 1980; 30:547-556 10.1099/00207713-30-3-547 - DOI - DOI - DOI
-
- Joyeux C, Fouchard S, Llopiz P, Neunlist S. Influence of the temperature and the growth phase on the hopanoids and fatty acids content of Frateuria aurantia (DSMZ 6220). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 2004; 47:371-379 10.1016/S0168-6496(03)00302-7 - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 1990; 215:403-410 - PubMed
-
- Korf I, Yandell M, Bedell J. BLAST, O'Reilly, Sebastopol, 2003.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

