Library construction for next-generation sequencing: overviews and challenges
- PMID: 24502796
- PMCID: PMC4351865
- DOI: 10.2144/000114133
Library construction for next-generation sequencing: overviews and challenges
Abstract
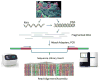
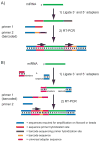
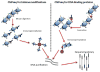
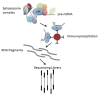
High-throughput sequencing, also known as next-generation sequencing (NGS), has revolutionized genomic research. In recent years, NGS technology has steadily improved, with costs dropping and the number and range of sequencing applications increasing exponentially. Here, we examine the critical role of sequencing library quality and consider important challenges when preparing NGS libraries from DNA and RNA sources. Factors such as the quantity and physical characteristics of the RNA or DNA source material as well as the desired application (i.e., genome sequencing, targeted sequencing, RNA-seq, ChIP-seq, RIP-seq, and methylation) are addressed in the context of preparing high quality sequencing libraries. In addition, the current methods for preparing NGS libraries from single cells are also discussed.
Keywords: ChIP-seq; DNA; DNA-seq; RIP-seq; RNA; RNA-seq; deep sequencing; library preparation; next-generation sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors DRS, SRH, and PO are founding scientists and consultants to Transplant Genomics Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Hashimshony T, Wagner F, Sher N, Yanai I. CEL-Seq: single-cell RNA-Seq by multiplexed linear amplification. Cell Rep. 2012;2:666–673. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
