Discovery of new liver X receptor agonists by pharmacophore modeling and shape-based virtual screening
- PMID: 24502802
- PMCID: PMC3934620
- DOI: 10.1021/ci400682b
Discovery of new liver X receptor agonists by pharmacophore modeling and shape-based virtual screening
Abstract
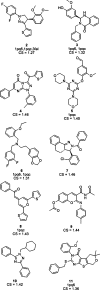
Agonists of liver X receptors (LXR) α and β are important regulators of cholesterol metabolism, but agonism of the LXRα subtype appears to cause hepatic lipogenesis, suggesting LXRβ-selective activators are attractive new lipid lowering drugs. In this work, pharmacophore modeling and shape-based virtual screening were combined to predict new LXRβ-selective ligands. Out of the 10 predicted compounds, three displayed significant LXR activity. Two activated both LXR subtypes. The third compound activated LXRβ 1.8-fold over LXRα.
Figures



References
-
- Ibanez B.; Vilahur G.; Cimmino G.; Speidl W. S.; Pinero A.; Choi B. G.; Zafar M. U.; Santos-Gallego C. G.; Krause B.; Badimon L.; Fuster V.; Badimon J. J. Rapid change in plaque size, composition, and molecular footprint after recombinant apolipoprotein A-I Milano (ETC-216) administration: Magnetic resonance imaging study in an experimental model of atherosclerosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, 1104–1109. - PubMed
-
- Nissen S. E.; Tsunoda T.; Tuzcu E. M.; Schoenhagen P.; Cooper C. J.; Yasin M.; Eaton G. M.; Lauer M. A.; Sheldon W. S.; Grines C. L.; Halpern S.; Crowe T.; Blankenship J. C.; Kerensky R. Effect of recombinant ApoA-I Milano on coronary atherosclerosis in patients with acute coronary syndromes: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA, J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2003, 290, 2292–2300. - PubMed
-
- Tardif J.-C.; Grégoire J.; L’Allier P. L.; Ibrahim R.; Lespérance J.; Heinonen T. M.; Kouz S.; Berry C.; Basser R.; Lavoie M.-A.; Guertin M.-C.; Rodés-Cabau J. Effects of reconstituted high-density lipoprotein infusions on coronary atherosclerosis: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA, J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2007, 297, 1675–1682. - PubMed
-
- Cuchel M.; Rader D. J. Macrophage reverse cholesterol transport: Key to the regression of atherosclerosis?. Circulation 2006, 113, 2548–2555. - PubMed
-
- Tall A. R. Cholesterol efflux pathways and other potential mechanisms involved in the athero-protective effect of high density lipoproteins. J. Intern. Med. 2008, 263, 256–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

